Exercise
Dumbbell Swing
The Dumbbell Swing is a fast, hip-driven exercise that builds explosive power, strengthens the lower body and quickly elevates your heart rate.
Dumbbell Swing
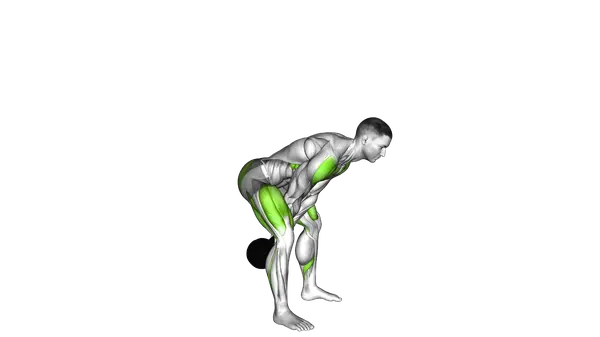
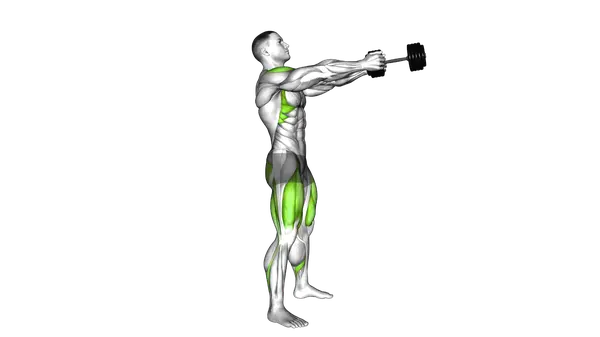
The Dumbbell Swing starts from a hip hinge, using a single dumbbell swung forward with force generated from the hips. The movement is driven by snapping the hips forward, not by lifting with the arms, while the upper body stays tall and controlled. At the top, the weight floats briefly before dropping back down between the legs.
This exercise trains the glutes and back of the legs while demanding strong core control and coordination. Because the movement is fast and rhythmic, it also places a high demand on your breathing and heart rate. You should feel a strong contraction in the hips as you stand tall and a stretch as the weight swings back.
Dumbbell swings are effective for building power, conditioning, and movement efficiency. You can make it easier by reducing the weight or slowing the pace, and harder by increasing load or maintaining a continuous rhythm for longer sets. Focus on crisp hip drive, keeping your arms relaxed, and controlling the swing path rather than muscling the weight up.
How to Perform the Dumbbell Swing
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a single dumbbell with both hands using an overhand grip, arms extended down in front of you.
- Slightly bend your knees, hinge at the hips, and allow the dumbbell to swing back between your legs while maintaining a flat back and engaged core.
- Forcefully drive your hips forward while keeping your arms straight, allowing momentum to swing the dumbbell up to chest or shoulder height.
- Exhale as you thrust your hips forward, keeping your shoulders pulled back and down away from your ears throughout the movement.
- Allow the dumbbell to naturally arc at the top of the movement without lifting with your arms or shoulders.
- As the dumbbell begins to descend, inhale and guide it back down by hinging at your hips again and slightly bending your knees.
- Control the descent as the dumbbell swings back between your legs, maintaining tension in your hamstrings and core.
- Immediately transition into the next repetition by driving your hips forward again, creating a continuous swinging motion.
Important information
- Keep your back flat throughout the entire movement, never rounding your lower back even at the bottom position.
- Drive the movement with your hip thrust, not by lifting with your arms or shoulders which can strain your lower back.
- Maintain a firm grip on the dumbbell, but avoid excessive tension in your upper body that might restrict fluid movement.
- Start with a lighter weight until you master the hip-hinge motion, as proper form is more important than heavy weight with this exercise.
FAQ - Dumbbell Swing
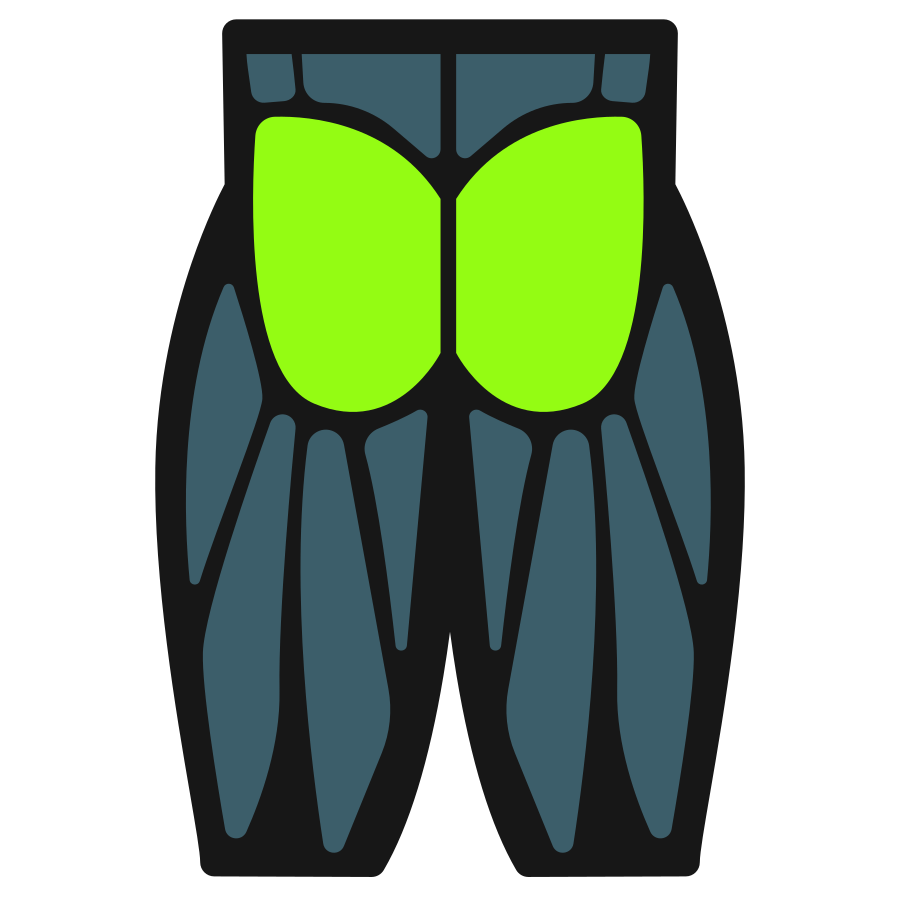
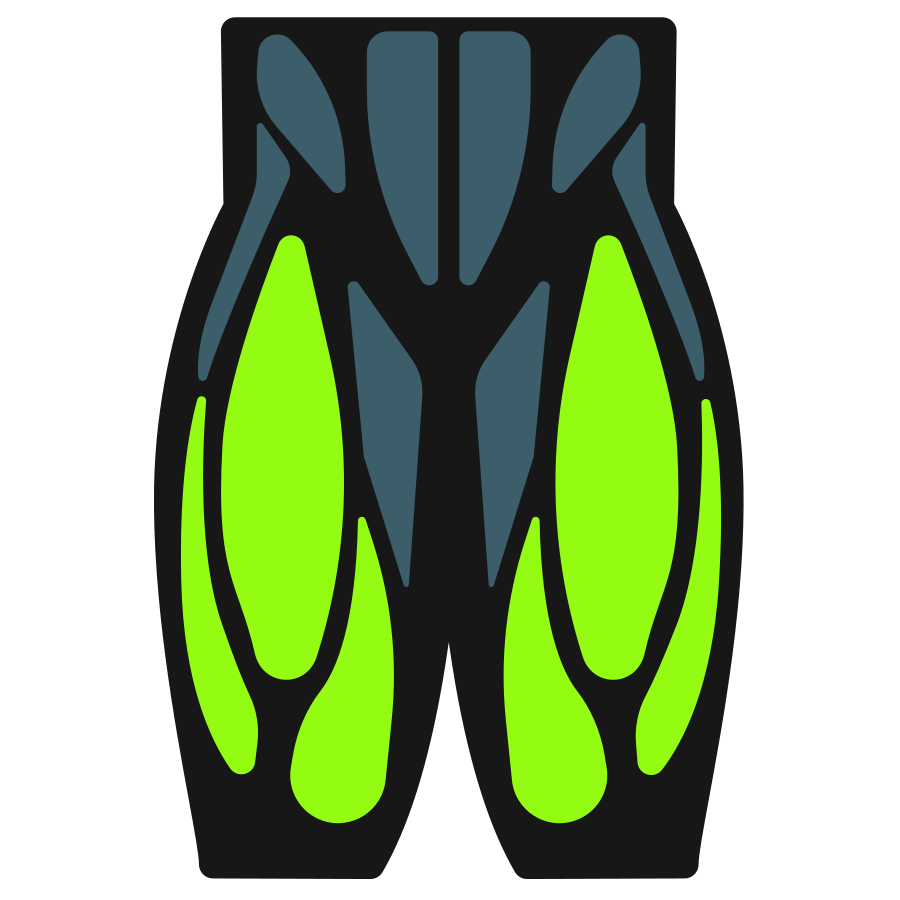
The dumbbell swing predominantly targets your posterior chain muscles, with the glutes serving as the main power generator. Your hamstrings work synergistically with the glutes, while your core remains constantly engaged to maintain proper spine position throughout the movement.
The dumbbell swing borrows the same movement pattern as the kettlebell swing but utilizes the more commonly available dumbbell. The main difference lies in hand positioning—you'll typically hold the dumbbell with both hands at one end, creating a slightly different weight distribution that may require more core stabilization.
The biggest mistake is squatting instead of hinging at the hips, which reduces posterior chain engagement and increases lower back strain. Other common errors include not generating power from the hips, lifting with the arms instead of letting them be passive, and allowing the back to round during the movement.
For an easier version, use a lighter weight and focus on perfecting the hip hinge pattern with a reduced range of motion. To increase difficulty, use a heavier dumbbell, increase repetitions, reduce rest periods, or incorporate the exercise into a HIIT circuit for greater metabolic demand.
You can safely perform dumbbell swings 2-3 times per week with at least 48 hours between sessions to allow your posterior chain to recover. They work exceptionally well as part of a metabolic conditioning circuit or as a power-building exercise at the beginning of a lower-body training session.

Dumbbell Swing
Exercise Details
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.