Maximize results in less time with high-intensity interval training
HIIT exercises
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) exercises are designed to push your body to its limits in short bursts, followed by brief recovery periods. This type of training is highly effective for fat loss, improving cardiovascular health, and boosting metabolism. Whether you’re training at home or in the gym, HIIT allows you to achieve significant fitness gains in a fraction of the time compared to traditional steady-state cardio.
Focus on
Pick your muscle groups
Pick your equipment
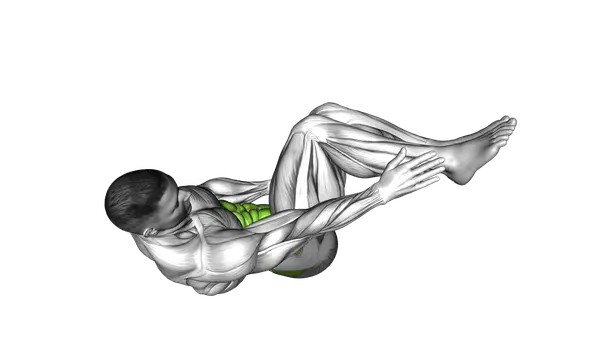
90 Degree Alternate Heel Touch
The 90 Degree Alternate Heel Touch trains controlled side bending, helping improve core control and coordination through slow, precise movement.

90 Degree Heel Touch
The 90 Degree Heel Touch builds controlled side-to-side core tension, helping improve stability and coordination with simple, steady movement.

Abdominal Air Bike
The Abdominal Air Bike is a bodyweight core exercise that combines controlled rotation with steady tension to build strength and endurance.

Alternate Heel Touchers
The Alternate Heel Touchers is a simple core exercise that builds control and endurance by using small side-to-side movements under tension.
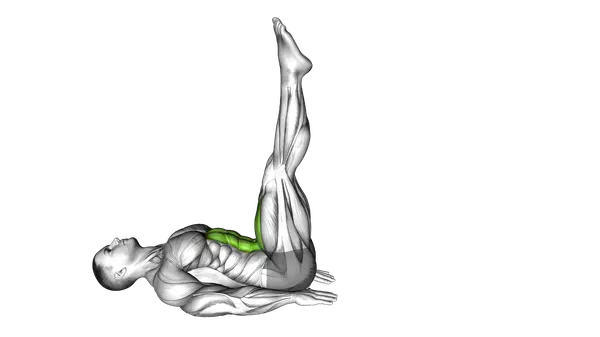
Alternate Leg Raise
The Alternate Leg Raise is a controlled core exercise that builds strength and stability by lifting one leg at a time while staying steady.
Built for Progress
Take the Guesswork Out of Training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward.

Alternate Lying Floor Leg Raise
The Alternate Lying Floor Leg Raise builds core control by lifting one leg at a time while keeping the lower body stable on the floor.

Assault Bike Run
The Assault Bike Run is a full-body conditioning movement that uses steady pedaling and pushing to build stamina and work capacity.

Assisted Pull-Up
The Assisted Pull-Up helps you build pulling strength by reducing bodyweight resistance, making it easier to learn proper pull-up technique and control.

Band Resisted Push Up
The Band Resisted Push Up is a push-up variation that increases upper-body strength by adding band resistance to the pressing movement.
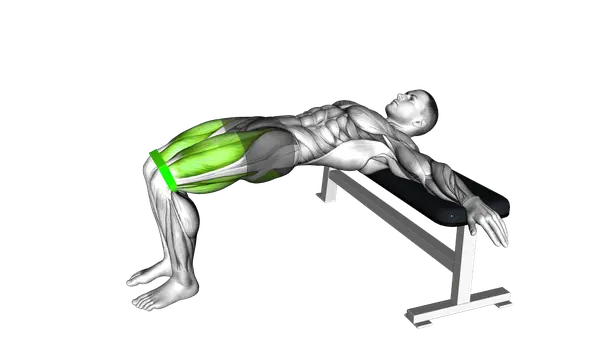
Banded Hip Thrusts
Banded Hip Thrusts are a lower-body strength exercise that builds glute power and tension through band resistance.

Barbell Lunge
The Barbell Lunge is a compound lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, balance and control through unilateral loading.

Barbell Step Up
The Barbell Step Up is a lower-body strength exercise that builds leg power, balance, and control through stepping under load.

Barbell Upright Row
The Barbell Upright Row is a compound lift that builds shoulder and upper-back strength by pulling a barbell vertically along the body.
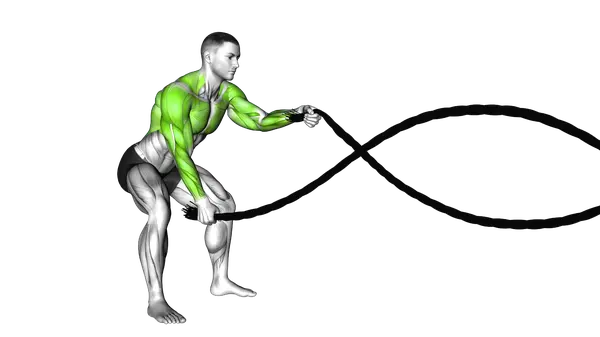
Battling Ropes
The Battling Ropes deliver a high-intensity full-body workout that builds endurance, power, and conditioning through continuous, explosive movement.
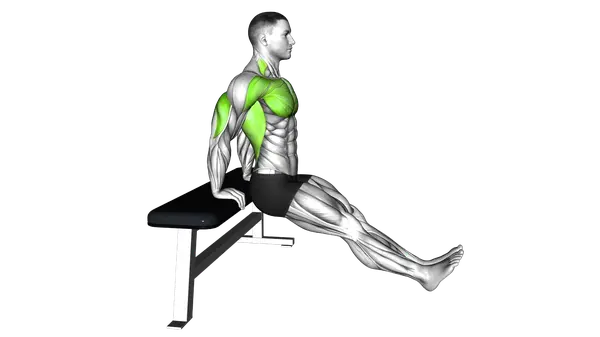
Bench Dip with heels on Floor
The Bench Dip with Heels on Floor is a bodyweight exercise used to build tricep strength while keeping the legs grounded for stability.
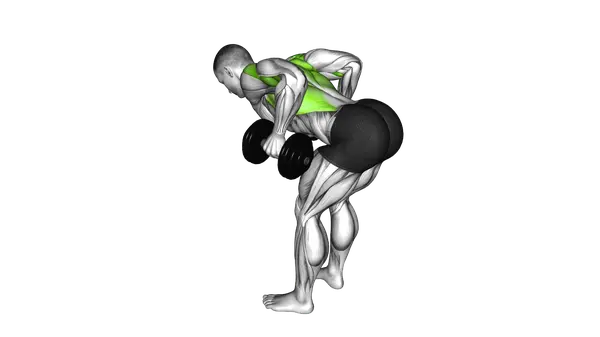
Bent Over Dumbbell Row
The Bent Over Dumbbell Row is a strength exercise that builds upper-back and arm strength using dumbbells in a hinged position.
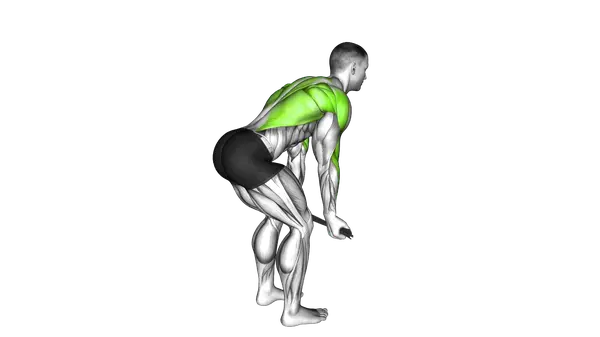
Bent Over Row With Towel
The Bent Over Row With Towel is a pulling exercise that builds upper-back strength while adding extra grip and control demand.
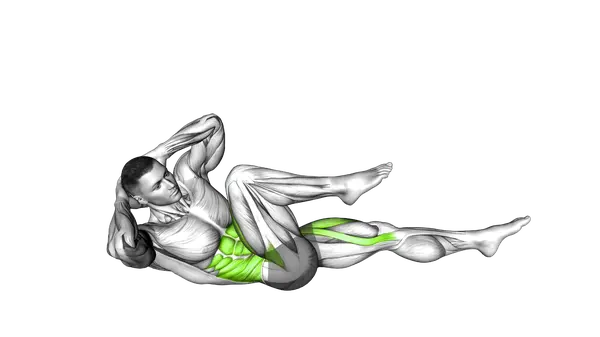
Bicycle Crunch
The Bicycle Crunch is a controlled core exercise that builds strength and coordination by combining rotation with alternating leg movement.

Bodyweight Full Squat With Overhead Press
The Bodyweight Full Squat With Overhead Press is a full-body exercise that builds leg strength, shoulder endurance and coordination.

Bodyweight Muscle Up
The Bodyweight Muscle Up is an advanced bodyweight exercise that combines pulling and pressing strength to move from hang to support.
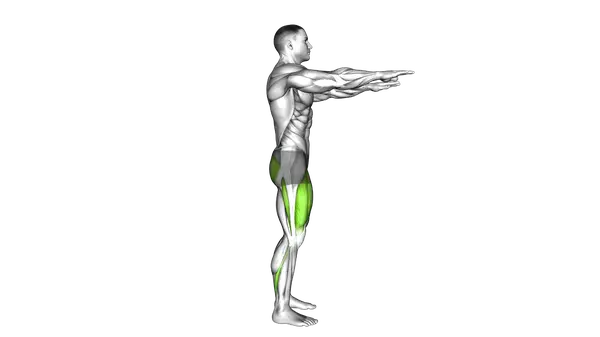
Bodyweight Squat
The Bodyweight Squat is a foundational lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, mobility and movement control.

Bodyweight Step Up
The Bodyweight Step Up is a lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, balance and control using a simple stepping motion.

Bulgarian Split Squat
The Bulgarian Split Squat is a lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, balance, and control by training one leg at a time.
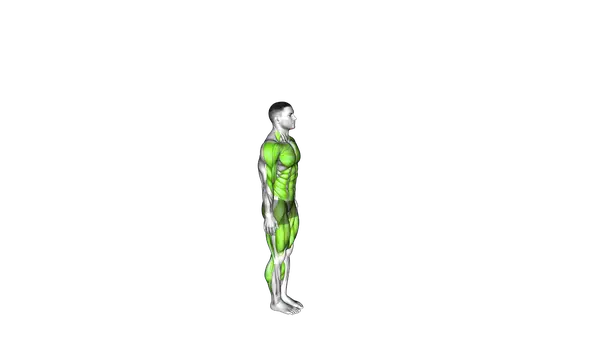
Burpee
The Burpee is a full-body exercise that builds conditioning, strength, and coordination through a fast, continuous movement.
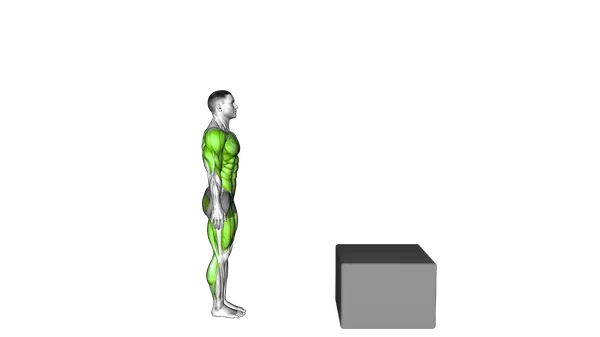
Burpee Box Jump
The Burpee Box Jump combines a burpee with an explosive box jump to build full-body power, coordination, and high-intensity conditioning.
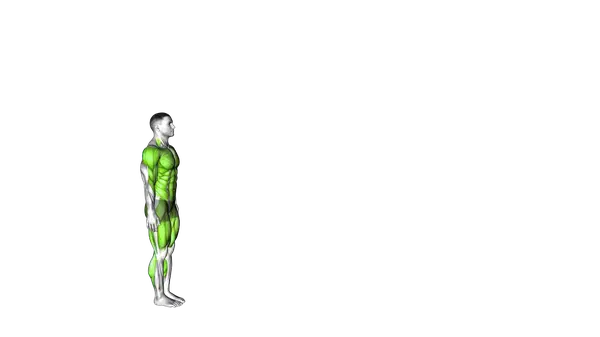
Burpee Broad Jump
The Burpee Broad Jump is a full-body exercise that combines a burpee with a forward jump to build power, conditioning, and total-body strength.
Increase fat loss, improve cardiovascular health, and build endurance
Training goals for HIIT development
HIIT is a time-efficient way to enhance both strength and cardiovascular fitness. These workouts elevate your heart rate quickly, forcing your body to burn more calories during and after the session (thanks to the afterburn effect, or EPOC). In addition to fat loss, HIIT training boosts endurance, cardiovascular health, and muscle tone by alternating between high-intensity movements and short rest periods. It’s perfect for individuals looking to get fitter without long training sessions.
Combine strength, cardio, and power in fast-paced circuits
Best HIIT exercises for fat loss and conditioning
The best HIIT exercises combine bodyweight movements, cardio, and strength work for full-body conditioning. Examples include burpees, jumping jacks, mountain climbers, squat jumps, and high knees. Kettlebell swings, sprint intervals, and battle rope exercises are also excellent for boosting intensity. These exercises target multiple muscle groups while keeping your heart rate elevated: the core principle behind HIIT’s effectiveness for fat loss and endurance.
Train with bodyweight, dumbbells, kettlebells, or cardio machines
Equipment options for HIIT training
One of the advantages of HIIT is its flexibility. While you can perform many HIIT exercises using just bodyweight, adding equipment like dumbbells, kettlebells, resistance bands, or cardio machines (rowers, bikes, treadmills) can increase intensity and variation. Dumbbells and kettlebells are ideal for adding resistance, while machines provide more consistent monitoring and control over intensity. HIIT workouts can easily be adapted for any fitness level or workout space.
Incorporate HIIT into your weekly routine for maximum efficiency
Training plans featuring HIIT exercises
HIIT can be performed 2–4 times per week, depending on your fitness level and goals. Since it’s a high-intensity workout, it’s important to balance HIIT with recovery, strength training, or lower-intensity sessions. You can structure your routine with a variety of exercises to target different muscle groups and avoid overtraining. The app helps you build a personalized HIIT plan based on your fitness goals, experience, and equipment. It ensures your routine is balanced, effective, and sustainable for long-term progress.
Frequently asked questions about HIIT exercises
Yes, warming up before HIIT is essential to prepare your muscles and cardiovascular system for the intensity of the workout. A proper warm-up increases blood flow, reduces the risk of injury, and prepares your body for explosive movements. Include dynamic stretches and light cardio, such as jogging or jumping jacks, before jumping into high-intensity intervals.
HIIT alternates between short bursts of high-intensity activity and rest or low-intensity periods, making it highly efficient for burning calories and building endurance in less time. Steady-state cardio, on the other hand, involves maintaining a consistent, moderate pace over a longer duration. While both types of training improve cardiovascular fitness, HIIT offers greater fat-burning potential and helps build both aerobic and anaerobic endurance.
Yes, many effective HIIT exercises can be done at home using only bodyweight. Bodyweight movements like burpees, jump squats, mountain climbers, and jumping jacks are highly effective for improving endurance and burning fat. If you want to increase intensity, you can add household items like a backpack or water bottles to create extra resistance.
Most people benefit from doing HIIT 2–3 times per week, allowing time for recovery in between. Since HIIT is intense, it’s important to avoid overtraining and provide your muscles with sufficient rest. Incorporating 1–2 days of moderate or low-intensity cardio or strength training can help balance the workload. Listen to your body and adapt frequency based on how you feel.
The best HIIT exercises include burpees, squat jumps, jumping jacks, mountain climbers, and high knees. These movements elevate your heart rate quickly while engaging multiple muscle groups. Kettlebell swings, sprints, and battle ropes are also highly effective for building strength and conditioning. A well-rounded HIIT routine combines both cardio and strength elements for maximum results.
Integrate HIIT exercises into full-body and split routines






