Exercise
Banded Hip Thrusts
Banded Hip Thrusts are a lower-body strength exercise that builds glute power and tension through band resistance.
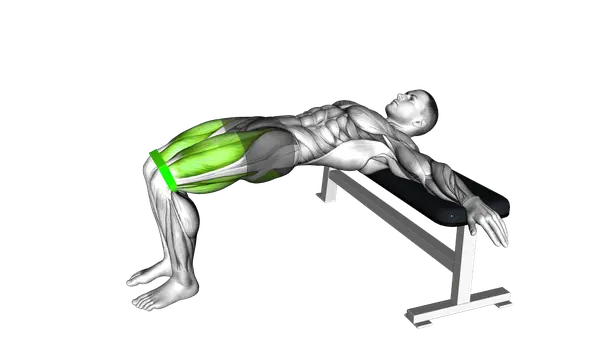
Banded Hip Thrusts
Banded Hip Thrusts are a compound lower-body exercise that use resistance bands to load the hip extension movement. The band increases tension as the hips rise, making the exercise effective for building strength and muscle control without heavy external weights.
The exercise primarily targets the glutes, with the hamstrings and core supporting hip extension and pelvic stability. Continuous band tension encourages strong muscle engagement at the top of the movement, where the glutes are most active.
Banded hip thrusts are commonly used in strength and hypertrophy programs, as well as warm-ups or accessory work for lower-body training days. Resistance level, volume, and tempo can be adjusted to match different training goals, making the exercise suitable for beginners and advanced lifters alike.
How to Perform the Banded Hip Thrusts
- Position yourself seated on the ground with your upper back against a bench, knees bent, and feet flat on the floor hip-width apart.
- Loop a resistance band around your hips and secure it under your feet or around a sturdy anchor point at floor level.
- Place your arms on the bench with palms down for stability, keeping your wrists neutral and fingers relaxed.
- Engage your core and tuck your chin slightly to maintain a neutral spine position throughout the movement.
- Inhale deeply, then as you exhale, drive through your heels to lift your hips toward the ceiling until your body forms a straight line from shoulders to knees.
- At the top position, squeeze your glutes maximally while keeping your ribcage down and maintaining tension in the resistance band.
- Hold the contracted position for 1-2 seconds while breathing normally, ensuring your knees stay aligned with your toes.
- Inhale as you slowly lower your hips back to the starting position with control, maintaining tension in your glutes throughout the descent.
Important information
- Keep your feet positioned directly under your knees at the top of the movement to maximize glute activation and minimize stress on the lower back.
- Avoid hyperextending your lower back at the top of the movement—focus on a posterior pelvic tilt by drawing your ribs down toward your pelvis.
- If you feel this exercise primarily in your hamstrings or lower back rather than your glutes, try moving your feet slightly farther from your body.
- Select a band with appropriate resistance—you should feel tension throughout the movement but still be able to achieve full hip extension with proper form.
FAQ - Banded Hip Thrusts
Banded hip thrusts primarily target the gluteus maximus (your largest glute muscle), while also engaging the hamstrings, hip flexors, and lower back as supporting muscles. The resistance band specifically intensifies activation at the top of the movement where your glutes are fully contracted.
Place the band just above your knees when sitting on the floor, then position yourself with your upper back against a bench, feet flat on the floor hip-width apart. Ensure the band remains taut throughout the movement, creating resistance as you drive your hips upward to full extension.
The three most common mistakes are hyperextending your lower back instead of using your glutes, failing to reach full hip extension at the top, and allowing your knees to cave inward against the band resistance. Focus on driving through your heels, maintaining neutral spine position, and actively pushing your knees outward against the band.
For optimal glute development, include banded hip thrusts 2-3 times weekly with at least 24 hours of recovery between sessions. You can program them as a primary lower-body movement on leg days or as a targeted glute activation exercise before other compound movements.
Progress by using thicker resistance bands, combining bands with barbell/dumbbell loading, elevating your feet to increase range of motion, or transitioning to single-leg variations. You can also manipulate tempo, adding a pause at the top position to increase time under tension in the fully contracted position.

Banded Hip Thrusts
Exercise Details
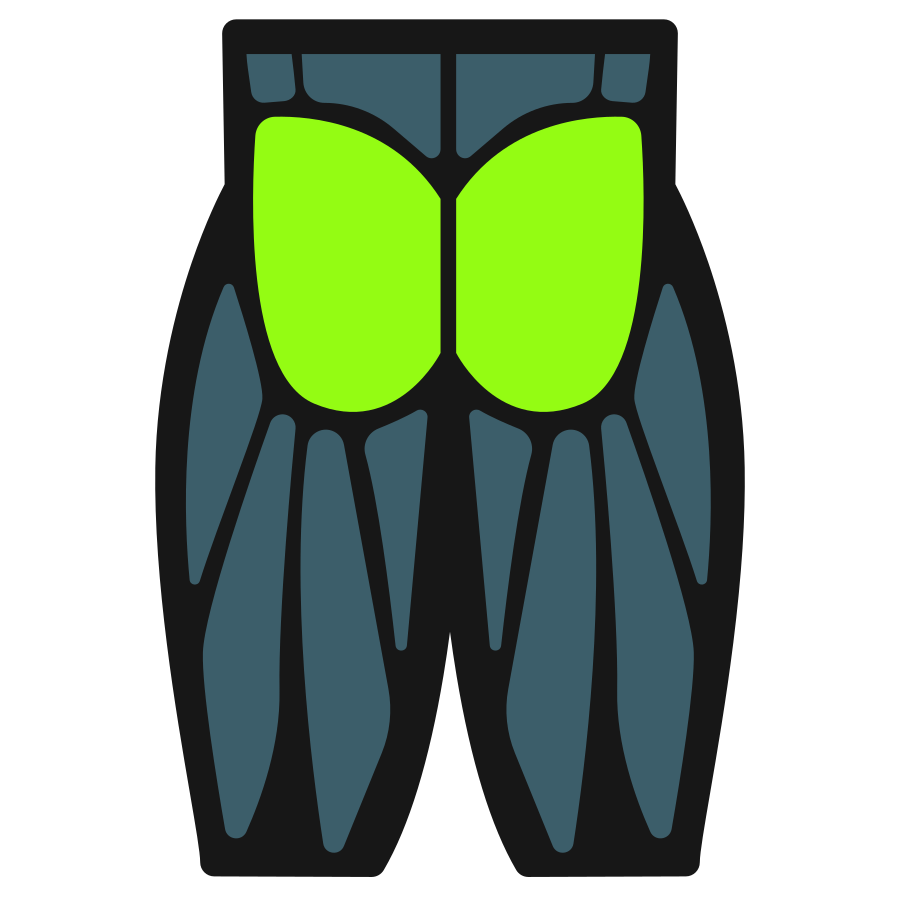
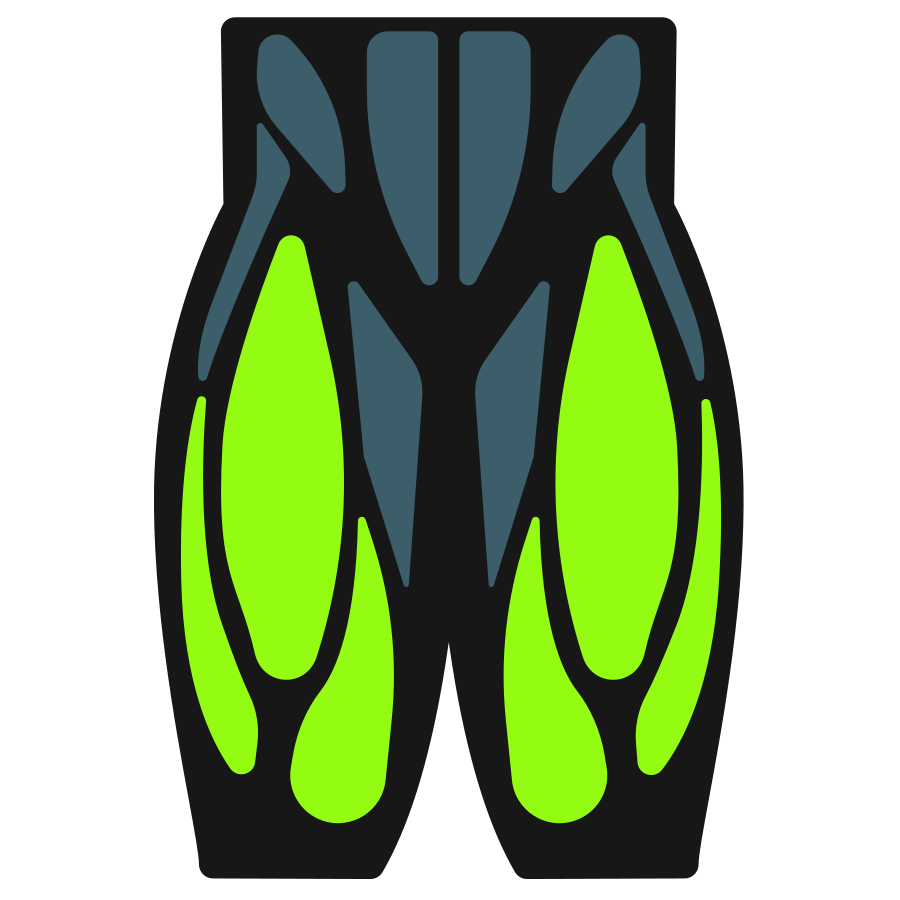
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.