Exercise
Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl
The Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl builds arm strength with controlled, alternating reps and constant tension on the biceps.

Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl
The Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl is a focused arm exercise that targets the biceps and forearms while minimizing momentum. Sitting on an incline bench places your arms slightly behind the body, increasing muscle stretch and making the movement more demanding than standard hammer curls.
Using a neutral grip (palms facing each other) shifts part of the load toward the brachialis and forearms, helping build thicker, stronger-looking arms. By curling one dumbbell at a time, you improve mind–muscle connection, balance left-to-right strength, and maintain better control throughout each rep.
This exercise is ideal for intermediate to advanced lifters looking to add variety to their arm training. It works especially well in hypertrophy-focused workouts, where slow tempo and strict form help maximize muscle activation without relying on heavy weights.
How to Perform the Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl
- Set an adjustable bench to a 30-45 degree incline and sit with your back firmly supported against the backrest, feet flat on the floor.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand with a neutral grip (palms facing each other), arms fully extended by your sides with elbows close to your torso.
- Maintain a neutral spine position with shoulders pulled back and down, chest up, and core engaged throughout the movement.
- Inhale and brace your core, then exhale as you curl one dumbbell up toward your shoulder while keeping your wrist in the neutral hammer position.
- Control the movement by focusing on contracting your bicep, raising the weight until your forearm is roughly parallel to the floor or slightly higher.
- Pause briefly at the top of the movement, squeezing your bicep while maintaining proper upper arm position with your elbow close to your side.
- Inhale as you slowly lower the dumbbell back to the starting position with control, ensuring you fully extend your arm without locking out the elbow.
- Alternate arms for each repetition, completing one full curl with one arm before switching to the other, maintaining tension in the biceps throughout the set.
Important information
- Keep your upper arms stationary throughout the movement – only your forearms should move to avoid recruiting the front deltoids.
- Maintain a neutral wrist position (hammer grip) during the entire exercise to target the brachialis and brachioradialis in addition to the biceps.
- Resist the urge to use momentum or swing the weights – slower, controlled movements maximize muscle engagement and reduce injury risk.
- If you experience wrist or elbow discomfort, try using lighter weights or adjusting your grip width slightly.
FAQ - Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl
This exercise primarily targets the brachialis and brachioradialis while still engaging the biceps brachii. The hammer grip significantly increases forearm activation, while the incline position creates greater tension on the biceps in their stretched state.
Set the bench to a 45-60 degree angle, sit with your back fully supported, and allow your arms to hang straight down with palms facing each other. Keep your shoulders pulled back and down throughout the movement to isolate the biceps and prevent shoulder involvement.
The three most critical errors are allowing the hips to sag (losing the pike position), shoulders rolling forward (compromising joint safety), and excessive body wobbling due to poor core bracing. Focus on maintaining a straight line from hands to hips, keeping shoulders packed away from ears, and engaging your core throughout the movement.
To make it easier, reduce the weight or switch to a half-kneeling position (one knee up). To increase difficulty, add more weight, slow down the eccentric (lowering) phase to 3-4 seconds, or progress to a tall kneeling position with knees close together to challenge core stability further.
For optimal results, incorporate this exercise 1-2 times weekly as part of your push or arm-specific training days. Since it's an isolation movement, it works best when programmed after compound exercises, using 3-4 sets of 8-15 repetitions depending on your specific goals.

Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl
Exercise Details
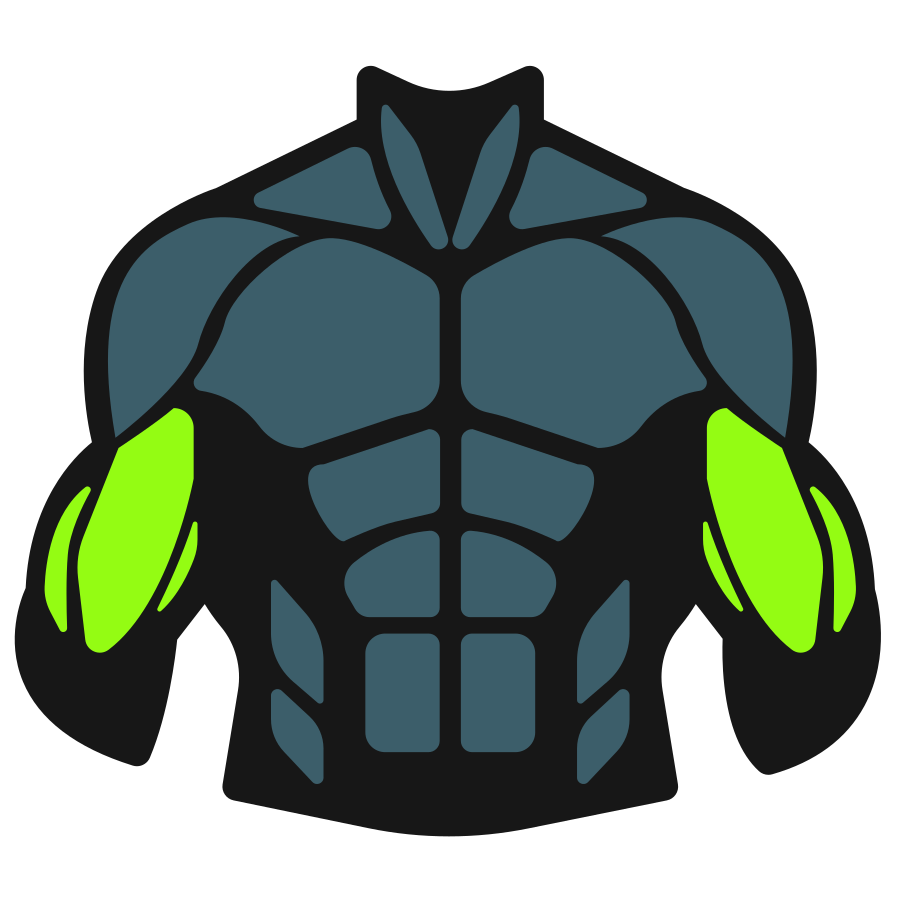
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.