Exercise
Barbell Bent Over Row
The Barbell Bent Over Row is a powerful compound exercise that builds back strength, improves posture and supports overall pulling performance.
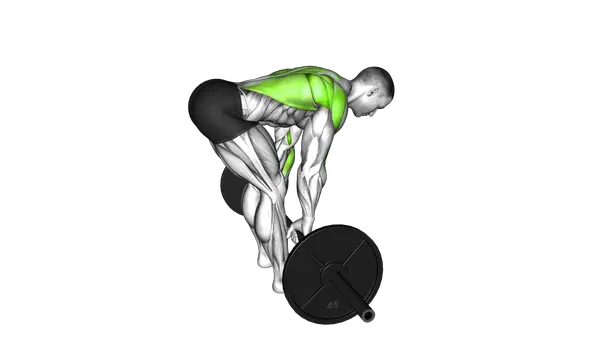
Barbell Bent Over Row
The Barbell Bent Over Row is a staple movement for developing a strong, balanced upper body. By pulling the barbell toward your torso from a hinged position, you train multiple muscle groups at once while reinforcing control and stability through your entire body. This makes it an efficient exercise for both strength-focused and performance-oriented training programs.
What sets this exercise apart is the constant tension created by maintaining a bent-over position throughout the movement. This demands focus on proper positioning, controlled motion, and consistent effort on every repetition. As a result, the exercise not only builds strength but also improves body awareness and coordination during pulling movements.
Because it allows for progressive loading, the Barbell Bent Over Row fits well into beginner, intermediate, and advanced routines. It can be used to build a strong foundation, support other lifts, or increase overall training volume for back-focused days. When performed with good technique, it delivers long-term benefits for strength, control, and resilience.
How to Perform the Barbell Bent Over Row
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and grasp the barbell with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder width.
- Hinge at your hips, keeping your back flat and chest up until your torso is nearly parallel to the floor.
- Allow the barbell to hang directly below your shoulders with your arms fully extended and your core braced.
- Take a deep breath in and hold it to maintain core tension.
- Pull the barbell toward your lower ribcage by driving your elbows back and squeezing your shoulder blades together.
- Keep your elbows close to your body and maintain a neutral wrist position throughout the movement.
- Exhale at the top of the movement, then slowly lower the barbell back to the starting position while maintaining control.
- Keep your torso angle consistent throughout all repetitions and avoid using momentum by jerking or swinging the weight.
Important information
- Keep your lower back in its natural arch and avoid rounding your spine at any point during the exercise.
- Maintain a slight bend in your knees to reduce stress on your lower back and hamstrings.
- Focus on pulling with your back muscles rather than your arms by initiating the movement by retracting your shoulder blades.
- If you feel pain in your lower back, decrease the weight or check your form with a qualified fitness professional.
FAQ - Barbell Bent Over Row
The barbell bent over row primarily targets the latissimus dorsi (lats) and trapezius muscles. It also engages the rhomboids, rear deltoids, biceps, and erector spinae as secondary muscles, making it one of the most complete upper back exercises available.
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, bend at the hips until your torso is nearly parallel to the floor, keep your back flat and core tight, then pull the barbell to your lower ribcage while keeping elbows close to your body. Lower the weight in a controlled manner and repeat, maintaining a neutral spine throughout the movement.
Maintain a neutral spine position (not rounded) and hinge properly at the hips rather than bending at the waist. Brace your core throughout the movement, avoid using excessive weight, and consider alternatives like chest-supported rows if pain persists despite form corrections.
Most lifters should perform bent over rows 1-2 times per week, allowing 48-72 hours of recovery between sessions. For optimal back development, include them as a primary movement on your pulling or back-focused training days.
Yes, effective alternatives include chest-supported rows, single-arm dumbbell rows, seated cable rows, and T-bar rows. These variations can reduce lower back stress while still targeting similar muscle groups, making them suitable replacements depending on your goals and equipment availability.

Barbell Bent Over Row
Exercise Details
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.