Exercise
Kettlebell Deadlift
The Kettlebell Deadlift is a simple hip hinge exercise that builds full lower-body strength while reinforcing safe lifting mechanics.
Kettlebell Deadlift
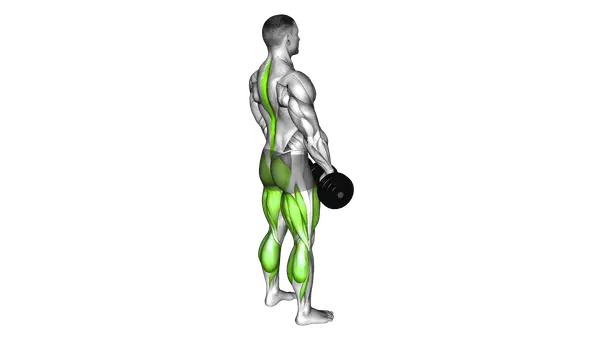
The Kettlebell Deadlift is a compound free-weight exercise where a kettlebell is lifted from the floor using a controlled hinge at the hips. The setup places the weight close to the body, making it accessible for learning proper pulling mechanics while still allowing meaningful strength development.
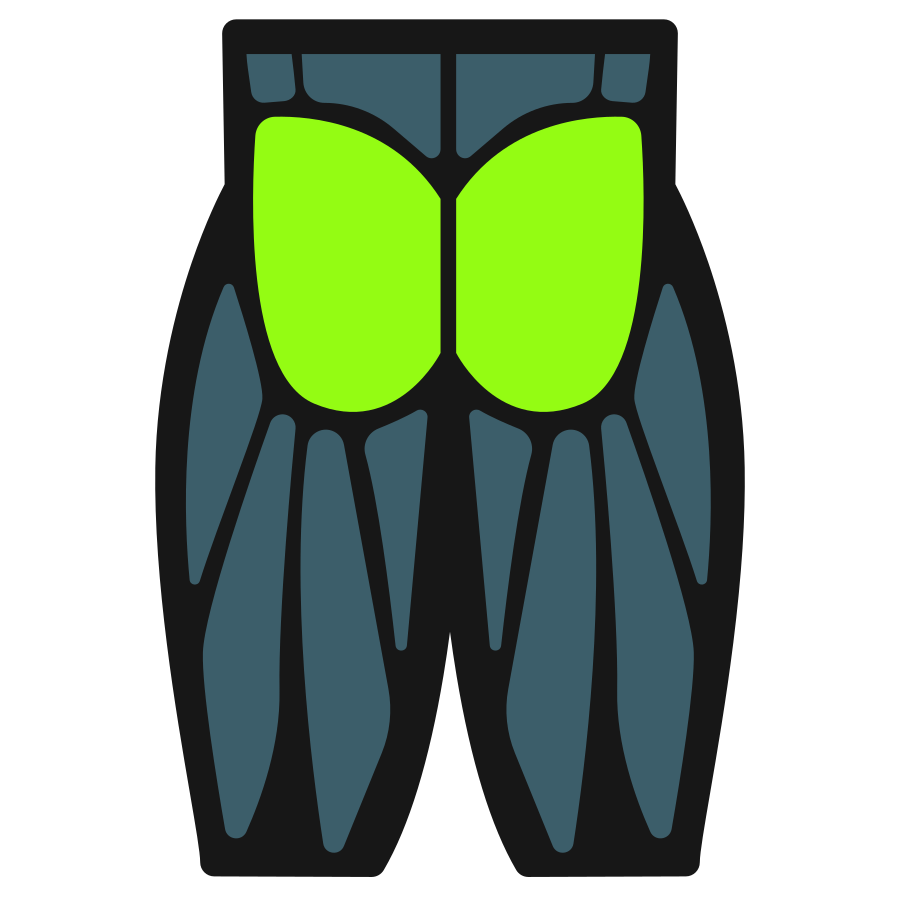
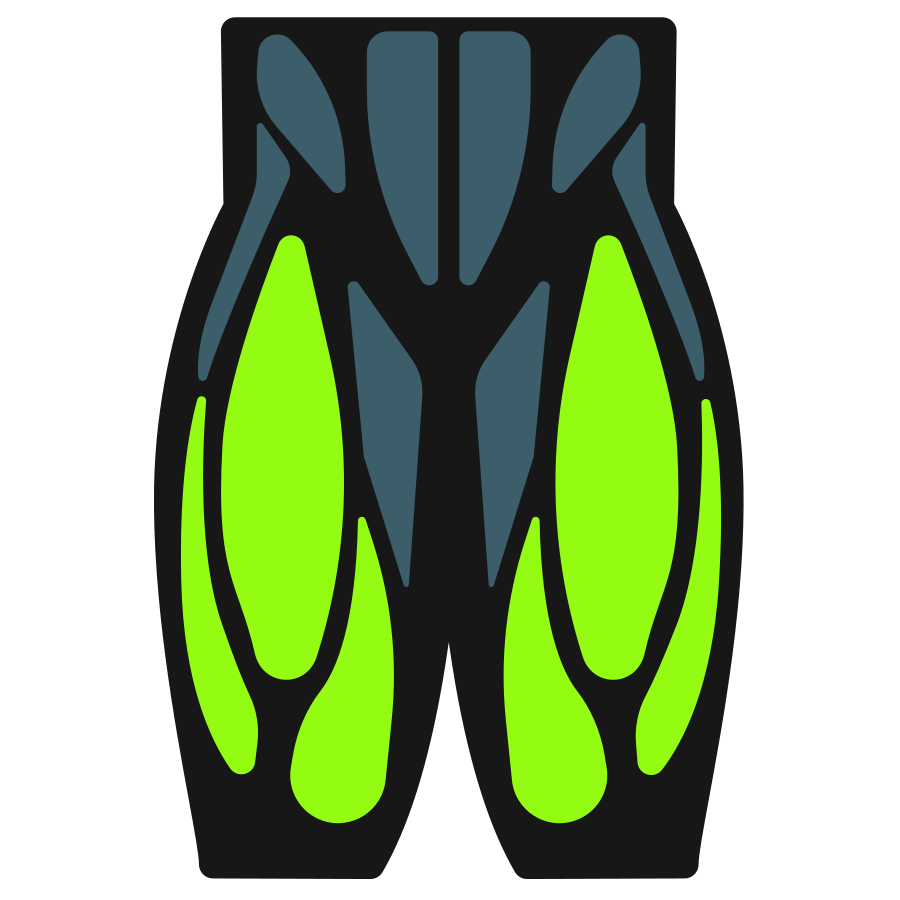
The exercise primarily targets the glutes and hamstrings, with the quads assisting during the initial lift from the floor. The back and core work to maintain a stable, neutral position, helping transfer force efficiently from the legs into the kettlebell.
Kettlebell Deadlift fits well in strength training, technique-focused sessions, and general fitness programs. It is especially useful for beginners learning deadlift patterns, but also works as a lighter or higher-rep alternative to barbell deadlifts for building consistency and control.
How to Perform the Kettlebell Deadlift
- Place a kettlebell between your feet, standing with feet shoulder-width apart and toes pointed slightly outward.
- Hinge at the hips by pushing your buttocks backward while maintaining a neutral spine, keeping your chest up and shoulders pulled back.
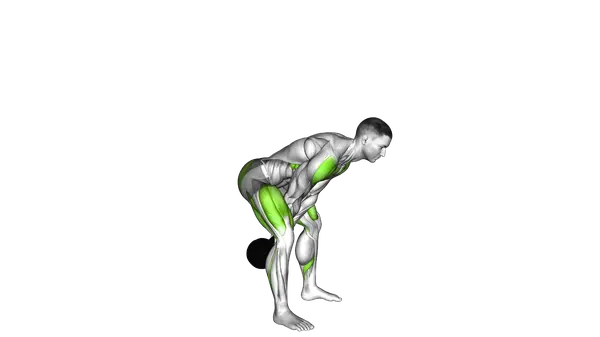
- Bend your knees slightly while reaching down to grasp the kettlebell handle with both hands, ensuring your back remains flat and your core engaged.
- Take a deep breath in and brace your core before initiating the lift.
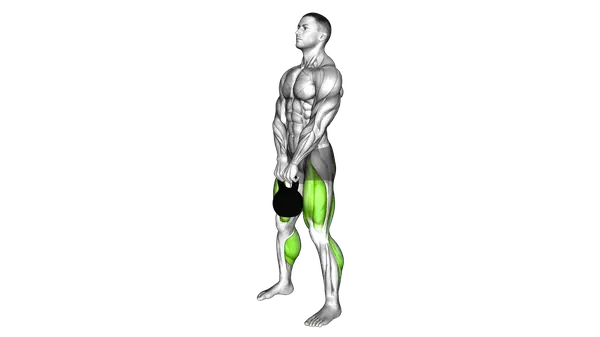
- Drive through your heels and extend your hips and knees simultaneously to stand up tall, exhaling as you rise while keeping the kettlebell close to your body.
- Achieve a full standing position with shoulders back, hips fully extended, and glutes squeezed at the top of the movement.
- To lower the weight, hinge at the hips first by pushing your buttocks backward, then bend your knees to return the kettlebell to the floor, inhaling during the descent.
- Touch the kettlebell to the ground between your feet before beginning the next repetition, maintaining tension in your core and back muscles throughout.
Important information
- Keep your back flat and neutral throughout the entire movement—never round your lower back or overarch.
- Position the kettlebell directly between your feet, not in front of them, to maintain proper balance and leverage.
- Drive through your heels rather than your toes to engage the posterior chain muscles effectively.
- If you feel any strain in your lower back, reduce the weight and focus on perfecting your hip hinge movement pattern.
FAQ - Kettlebell Deadlift
The Kettlebell Deadlift primarily targets your posterior chain, including the glutes, hamstrings, and erector spinae (lower back muscles). It also engages your core, traps, and forearms as stabilizing muscles throughout the movement.
The Kettlebell Deadlift places the weight between your legs rather than in front of you, creating a more centered load pattern that's often easier on the lower back. The kettlebell's design also creates a different grip challenge and typically allows for greater range of motion compared to a barbell variation.
The most common mistakes include rounding the lower back, failing to hinge properly at the hips, and lifting with the arms instead of driving through the legs. Always maintain a neutral spine, push your hips back before bending your knees, and think about "pushing the floor away" with your feet as you stand up.
For beginners, start with a kettlebell that allows you to complete 10-12 reps with proper form—typically 35-53 lbs (16-24 kg) for men and 26-35 lbs (12-16 kg) for women. Intermediate lifters should choose a weight that challenges them in the 6-10 rep range while maintaining perfect technique.
Incorporate Kettlebell Deadlifts 1-3 times weekly, allowing at least 48 hours between sessions for recovery of the posterior chain muscles. For strength development, perform them early in your workout when fresh, using 3-5 sets of 5-10 repetitions.

Kettlebell Deadlift
Exercise Details
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.