Exercise
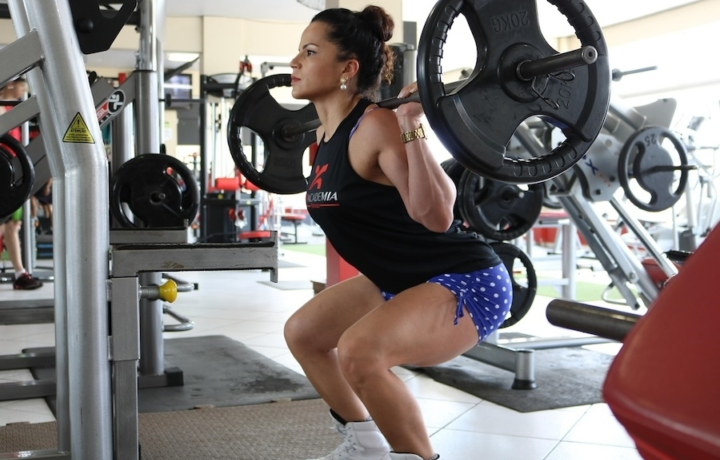
Barbell Front Squat
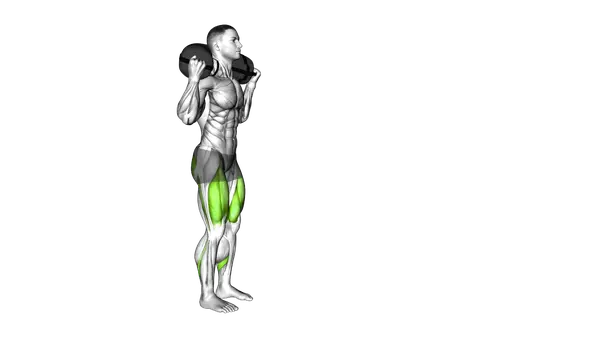
The Barbell Front Squat is a lower-body strength exercise that builds quad strength while reinforcing an upright, stable squat position.

Barbell Front Squat
The Barbell Front Squat is a compound barbell exercise where the load is held in front of the shoulders, shifting emphasis toward the front of the lower body. This front-loaded position promotes an upright torso and reduces reliance on the lower back compared to back squat variations.
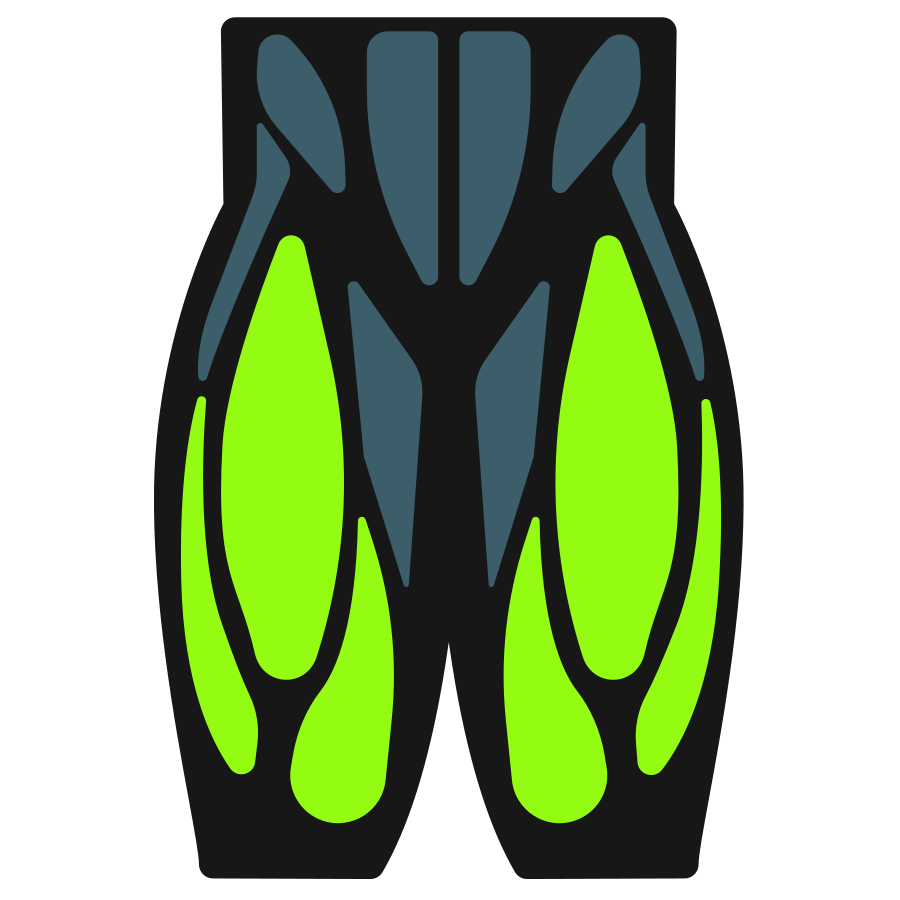
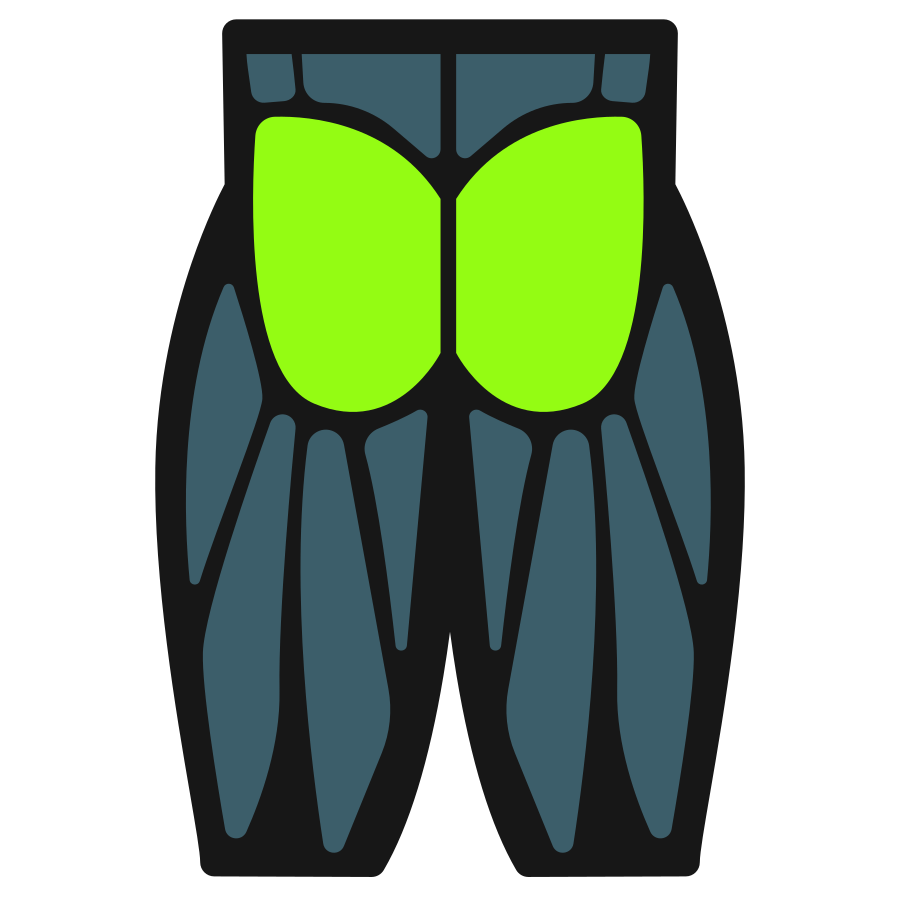
The exercise primarily targets the quadriceps, with the glutes contributing to hip extension and the core working to stabilize the torso under load. Upper-back and arm engagement help maintain the bar position, encouraging controlled movement and balanced force production.
The barbell front squat is commonly used in strength and hypertrophy programs, as well as Olympic lifting and athletic training. It is especially useful for building quad-dominant leg strength, improving squat mechanics, and developing lower-body power with controlled spinal loading.
How to Perform the Barbell Front Squat
- Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, position the barbell on your front deltoids with elbows high and pointing forward, creating a shelf with your shoulders.
- Establish a grip slightly wider than shoulder-width, with fingers under the bar and wrists extended, keeping your upper arms parallel to the floor.
- Brace your core and take a deep breath in, maintaining a tall chest position and neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Begin the descent by breaking at the hips and knees simultaneously, keeping your weight distributed evenly through your entire foot.
- Lower your body until your thighs are at least parallel to the ground, while keeping your elbows up and torso as vertical as possible.
- At the bottom position, ensure your knees track in line with your toes and your heels remain firmly planted on the ground.
- Drive through your midfoot and heels to push yourself back up, exhaling as you pass the sticking point while maintaining your upright torso position.
- Fully extend your hips and knees at the top position without hyperextending your back, then reset your breath and core before beginning the next repetition.
Important information
- Keep your elbows high throughout the entire movement to prevent the bar from rolling forward off your shoulders.
- If wrist mobility is limiting your front rack position, try using a cross-arm grip or specialized lifting straps.
- Maintain an upright torso position more vertical than in a back squat to properly load the quadriceps and prevent the bar from falling forward.
- Start with lighter weights than you would use for back squats until you've mastered the front rack position and movement pattern.
FAQ - Barbell Front Squat
The barbell front squat primarily targets the quadriceps, while also engaging the glutes, adductors, and core muscles intensely. The front rack position creates greater quad activation compared to back squats, while maintaining significant glute recruitment and demanding superior core stability to maintain an upright torso.
Rest the barbell across your front deltoids with fingers under the bar in a clean grip position, elbows pointed forward and up at shoulder height. If wrist mobility is limited, you can use the cross-arm position where arms cross in front of you with the bar resting on your deltoids and hands holding the bar in place.
Yes, front squats typically place less shear force on the lumbar spine due to the more vertical torso position required. This makes them an excellent option for lifters with back concerns who still want to train heavy, though proper form remains crucial regardless of squat variation.
For intermediate lifters, incorporating front squats 1-2 times weekly allows for adequate recovery while promoting strength gains. You can program them as your primary squat movement on quad-focused days or as an accessory exercise after back squats, adjusting volume based on your recovery capacity.
The most common mistakes include dropping the elbows (causing the bar to roll forward), excessive forward lean, and allowing knees to collapse inward. Focus on maintaining high elbows throughout the movement, keeping your torso as upright as possible, and driving your knees outward in line with your toes during both descent and ascent.

Barbell Front Squat
Exercise Details
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.