Exercise
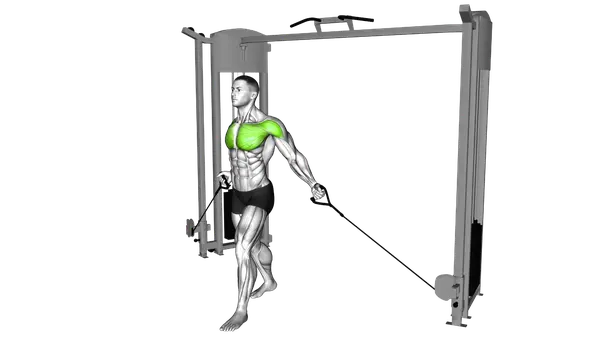
Cable Low to High Cable Fly
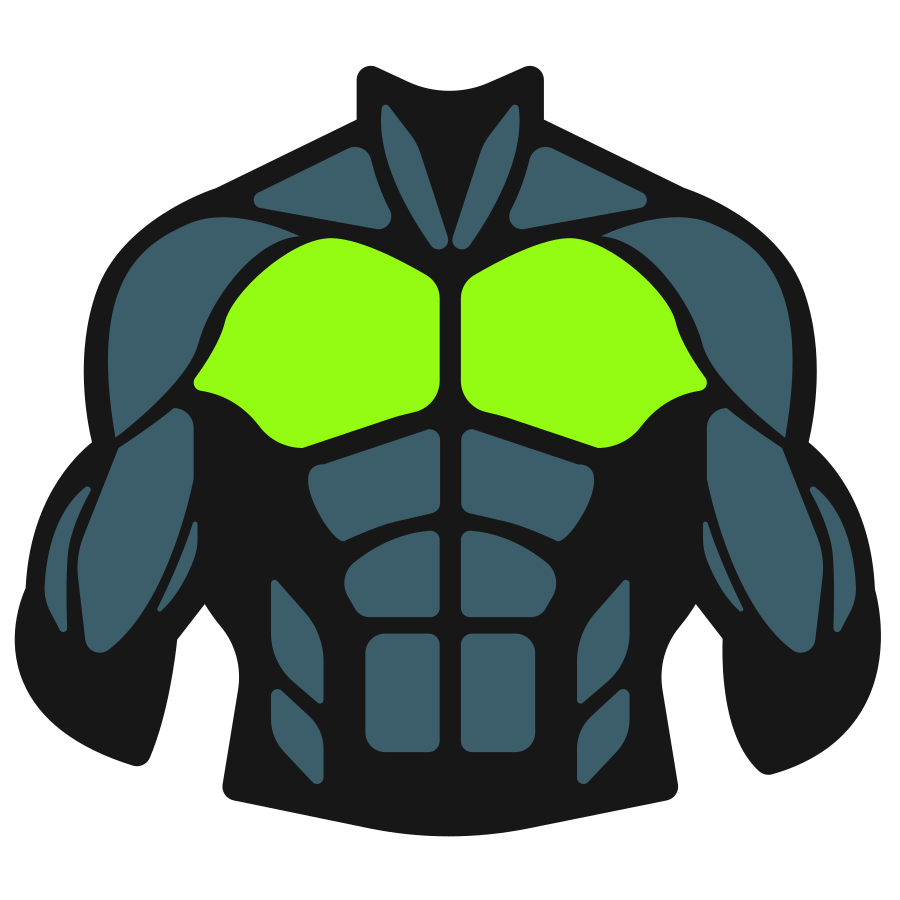
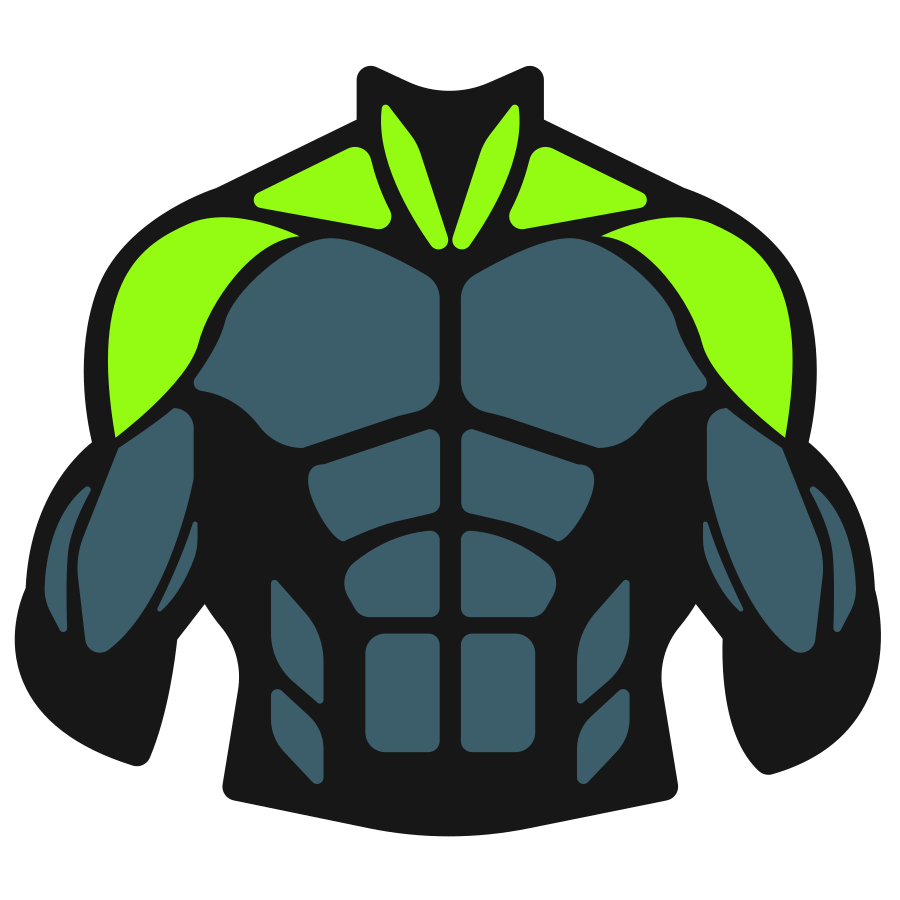
The Cable Low to High Cable Fly is a chest isolation exercise that targets the upper chest by guiding the arms upward through a controlled cable motion.
Cable Low to High Cable Fly
The Cable Low to High Cable Fly is a chest-focused isolation exercise that emphasizes the upper portion of the chest. Using cables allows for constant tension throughout the movement, helping maintain muscle engagement from start to finish.
By moving the handles from a low position to a higher finish, the exercise follows a natural pressing path that supports controlled chest activation while minimizing momentum. This makes it especially effective for developing upper chest definition and improving mind-muscle connection.
The Cable Low to High Cable Fly is commonly used in bodybuilding and hypertrophy-focused training programs. It is often programmed after compound presses to add targeted volume to the chest and support balanced chest development.
How to Perform the Cable Low to High Cable Fly
- Adjust the cable pulleys to the lowest position and select an appropriate weight for your level, then stand in the center of the cable machine with your feet shoulder-width apart and your core engaged.
- Grasp a handle in each hand and step forward slightly, maintaining a slight bend in your knees and a neutral spine position.
- Begin with your arms extended down and slightly in front of your body, with a slight bend in your elbows and palms facing forward.
- Brace your core and exhale as you pull the cables upward and inward in a wide arc motion, bringing your hands together at about eye level.
- Keep your elbows slightly bent throughout the movement, maintaining the same angle from start to finish to maximize chest engagement.
- At the top of the movement, squeeze your chest muscles for 1-2 seconds while maintaining proper posture and avoiding excessive leaning backward.
- Inhale as you slowly return to the starting position in a controlled manner, following the same arc path and feeling the stretch across your chest.
- Maintain tension on the cables throughout the entire exercise, never allowing the weight stack to rest between repetitions.
Important information
- Avoid locking your elbows at any point during the exercise as this shifts tension away from the chest muscles and can stress the joints.
- Focus on moving your arms in an arc pattern rather than a straight line to properly engage the chest fibers.
- Keep your shoulders pulled back and down throughout the movement to prevent unnecessary strain on your shoulder joints.
- If you feel excessive strain in your shoulders rather than your chest, reduce the weight and check your form before continuing.
FAQ - Cable Low to High Cable Fly
The Cable Low to High Fly primarily works the pectoral muscles, with emphasis on the upper and inner chest regions. It also engages the anterior deltoids (front shoulders) as secondary movers and recruits core muscles for stabilization throughout the movement.
Stand facing the cable machine with a staggered stance for stability, keep your upper arms close to your ears throughout the movement, and focus on extending only at the elbow joint while maintaining a stable torso. The movement should come solely from your elbows, not your shoulders or back.
Increase the resistance gradually as you master the movement pattern. Try slowing down the eccentric (lowering) phase to 3-4 seconds, incorporate brief isometric holds at the point of maximum contraction, or perform drop sets by immediately reducing weight when you reach failure for extended time under tension.
Unlike flat bench flies that move horizontally, the Low to High Cable Fly's diagonal movement pattern creates unique activation across the upper chest fibers. The cable mechanism also provides constant tension throughout the entire range of motion, whereas dumbbells lose resistance at certain points of traditional flies.
Incorporate this exercise 1-2 times weekly as part of your chest training. Position it after compound movements like bench press or as part of a superset to maximize muscle fiber recruitment. For hypertrophy, aim for 3-4 sets of 10-15 reps with moderate weight and focus on maintaining perfect form.

Cable Low to High Cable Fly
Exercise Details
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.














