Exercise
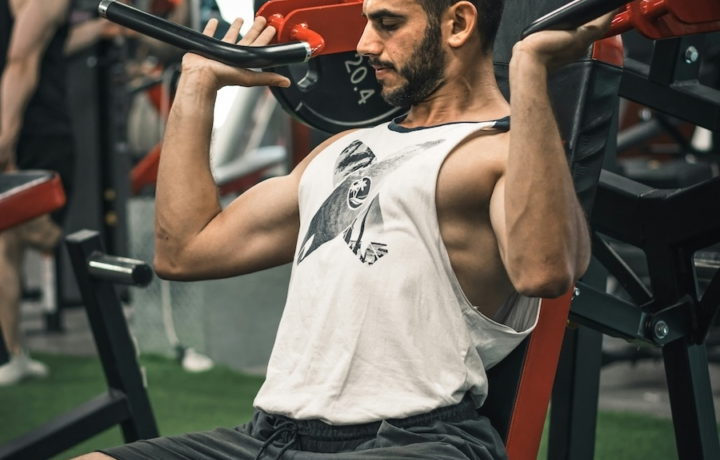
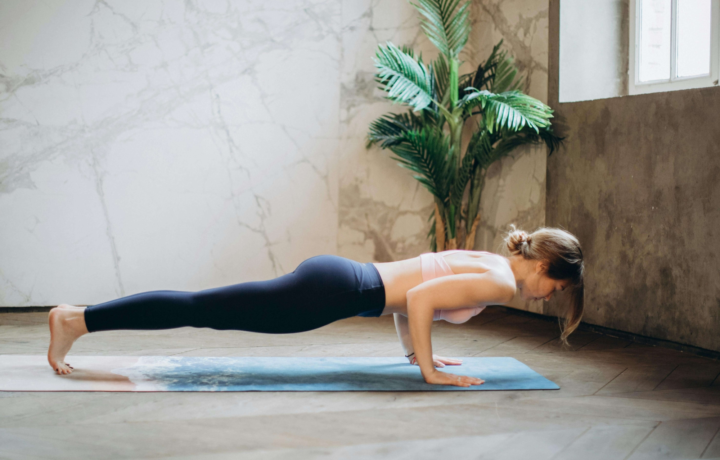
Push-Up
The Push-Up is a classic bodyweight exercise that builds strength, control, and full-body stability using only your own weight.

Push-Up
The Push Up trains your upper body while forcing your core and legs to stay engaged throughout the entire rep. By keeping your body in a straight line, the push up encourages strong posture and controlled movement from start to finish.
Because it can be adjusted easily, the push up works for all fitness levels. Changing hand position, tempo, or body angle allows you to make the exercise easier or more challenging without adding equipment, making it highly versatile.
Push ups fit seamlessly into strength workouts, conditioning circuits, or warm-up routines. Whether used for high repetitions or slow, controlled reps, they remain one of the most effective exercises for building pressing strength and overall body control.
How to Perform the Push-Up
- Begin in a plank position with your hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, arms fully extended, and palms flat on the floor.
- Position your feet together or slightly apart for stability, keeping your body in a straight line from head to heels, and engage your core.
- Inhale as you slowly bend your elbows to lower your chest toward the floor, keeping them at approximately a 45-degree angle from your body.
- Maintain a neutral spine position throughout the movement, avoiding sagging hips or an arched back.
- Lower yourself until your chest is about 1-2 inches from the floor or as far as your strength allows while maintaining proper form.
- Exhale as you push through your palms to straighten your arms and return to the starting position, fully extending your elbows without locking them.
- Keep your neck in a neutral position by looking slightly ahead of your hands rather than up or down.
- Squeeze your chest muscles at the top of the movement before beginning your next repetition, maintaining tension throughout your core and glutes.
Important information
- Keep your elbows from flaring out too wide, as this places excessive stress on your shoulder joints; aim for that 45-degree angle from your body.
- Maintain a rigid body position throughout the exercise — if your hips sag or pike up, reduce the difficulty or try an elevated variation.
- If you're a beginner, start with modified push-ups from your knees or with hands elevated on a bench until you build enough strength for the full version.
- Focus on quality over quantity, performing each repetition with proper technique rather than rushing through with poor form.
FAQ - Push-Up
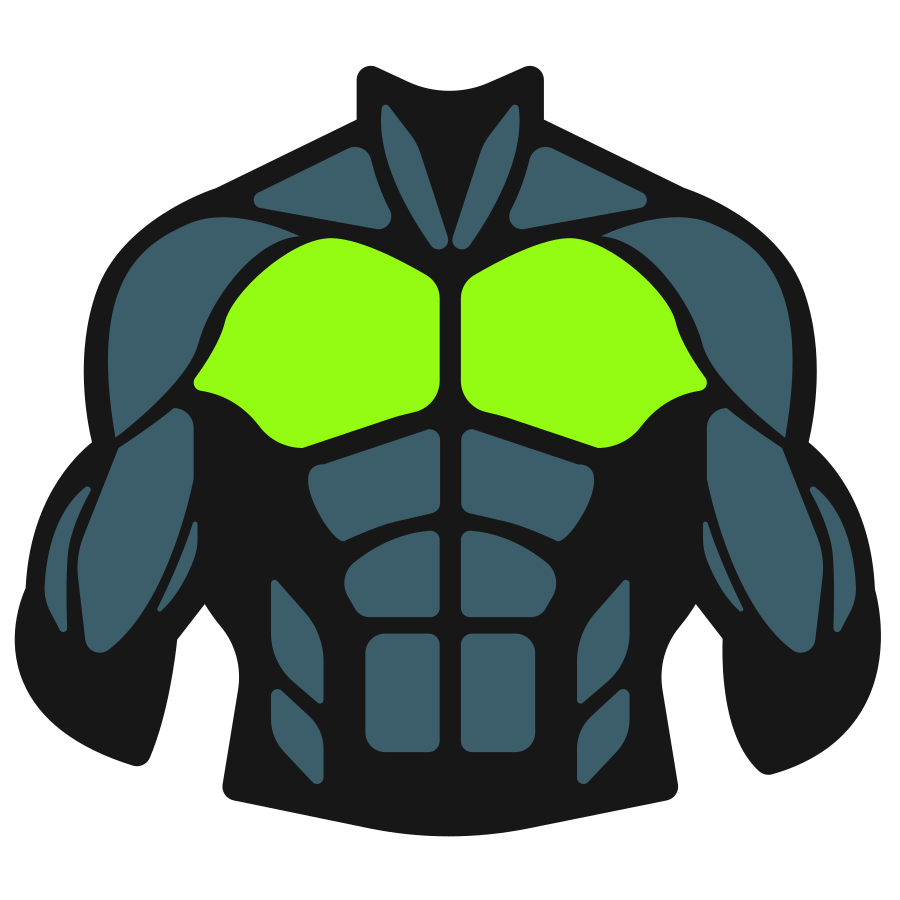
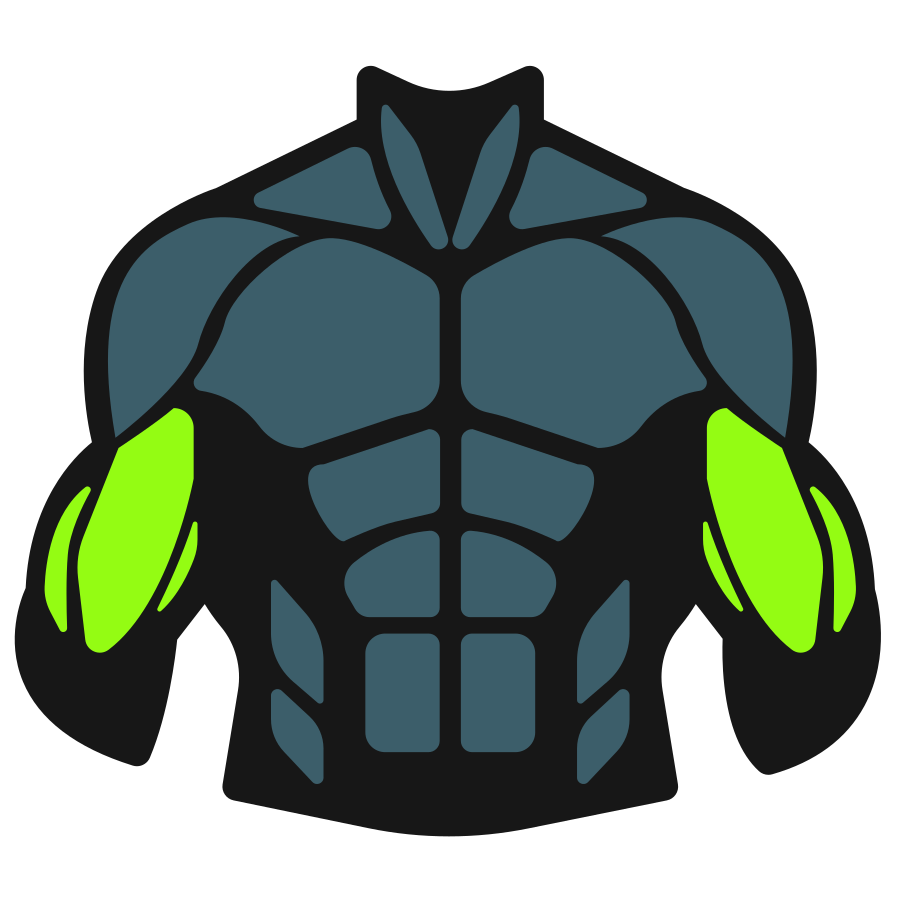
Push-ups primarily target your pectoral muscles (chest), while also engaging your triceps and anterior deltoids (front shoulders) as secondary movers. Your core muscles, including the abdominals and lower back, work as stabilizers throughout the movement.
Beginners can start with knee push-ups (keeping knees on the ground) or incline push-ups with hands elevated on a bench, chair, or wall. These variations reduce the amount of body weight you're lifting, making the exercise more manageable while you build strength.
The most common mistakes include sagging or hiking the hips, flaring the elbows too far out, not going through full range of motion, and improper head position. Keep your body in a straight line from head to heels, position elbows at about 45 degrees from your body, and lower your chest nearly to the floor.
Increase difficulty by elevating your feet, adding a weight plate on your back, wearing a weighted vest, using unstable surfaces like medicine balls, or trying advanced variations like decline, diamond, archer, or one-arm push-ups. Slowing down the tempo also significantly increases intensity.
For strength development, aim for 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions with proper form, 2-3 times per week. For endurance, increase to 15-25 reps per set. Allow at least 48 hours between intense push-up sessions to let your chest and triceps recover properly.

Push-Up
Exercise Details
Primary Muscles
Secondary Muscles
Muscle Groups
Mechanic
Risk Areas
Built for progress
Take the guesswork out of training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward, one workout at a time.