Exercises to strengthen grip, control and forearm development
Forearm exercises
Forearm exercises are crucial for building strong, stable wrists and a powerful grip. While often overlooked, the forearms play a key role in nearly every upper body movement: from pulling and lifting to stabilizing during pressing. Well-developed forearms not only improve functional performance but also add to your overall arm aesthetics. Whether you’re an athlete or recreational lifter, regular forearm training enhances control, endurance, and injury resilience.
Focus on
Pick your equipment

Alternate Standing Dumbbell Curl
The Alternate Standing Dumbbell Curl builds arm strength by lifting one weight at a time, helping improve control and balance between sides.

Assisted Pull-Up
The Assisted Pull-Up helps you build pulling strength by reducing bodyweight resistance, making it easier to learn proper pull-up technique and control.
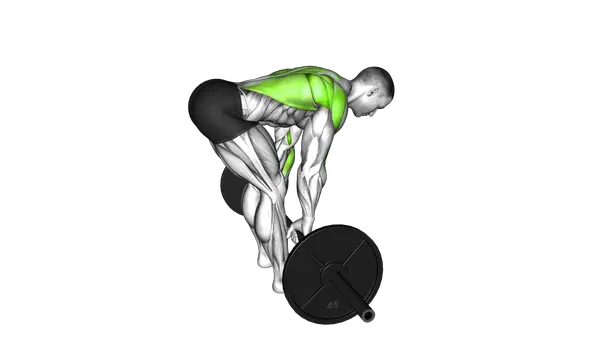
Barbell Bent Over Row
The Barbell Bent Over Row is a powerful compound exercise that builds back strength, improves posture and supports overall pulling performance.

Barbell Curl
The Barbell Curl is a basic arm exercise that builds strength and size by lifting a bar through a controlled bending motion.

Barbell Upright Row
The Barbell Upright Row is a compound lift that builds shoulder and upper-back strength by pulling a barbell vertically along the body.
Built for Progress
Take the Guesswork Out of Training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward.

Barbell Wrist Curl
The Barbell Wrist Curl is a simple forearm exercise that builds grip strength and control by isolating wrist movement under light to moderate load.

Barbell Wrist Reverse Curl
The Barbell Wrist Reverse Curl targets the top of the forearms, improving wrist control and balanced grip strength through strict, controlled movement.
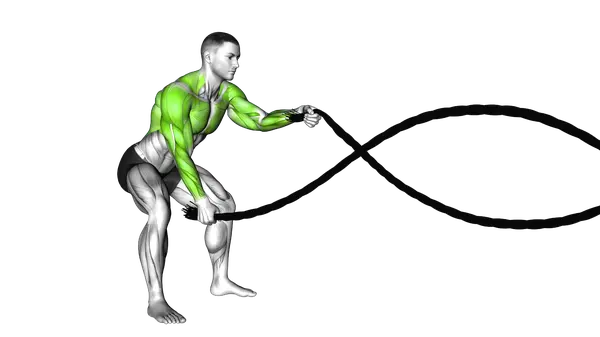
Battling Ropes
The Battling Ropes deliver a high-intensity full-body workout that builds endurance, power, and conditioning through continuous, explosive movement.
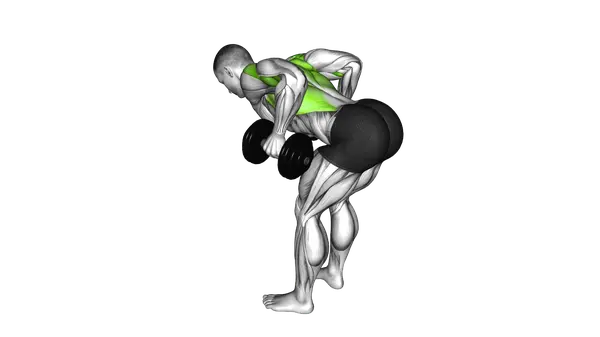
Bent Over Dumbbell Row
The Bent Over Dumbbell Row is a strength exercise that builds upper-back and arm strength using dumbbells in a hinged position.
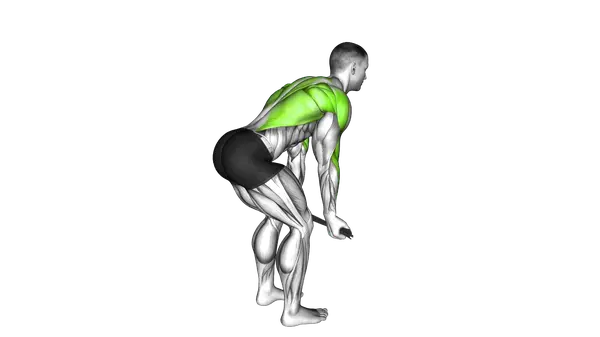
Bent Over Row With Towel
The Bent Over Row With Towel is a pulling exercise that builds upper-back strength while adding extra grip and control demand.

Bodyweight Muscle Up
The Bodyweight Muscle Up is an advanced bodyweight exercise that combines pulling and pressing strength to move from hang to support.

Cable Curl
The Cable Curl is a controlled arm exercise that builds steady biceps strength using constant tension from the cable machine.

Chin-Up
The chin-up is a bodyweight pulling exercise that builds upper-back and arm strength using an underhand grip and controlled movement.

Dumbbell Bent Over Wide Row
The Dumbbell Bent Over Wide Row targets the upper back and rear shoulders, helping build back width, strength and posture control.
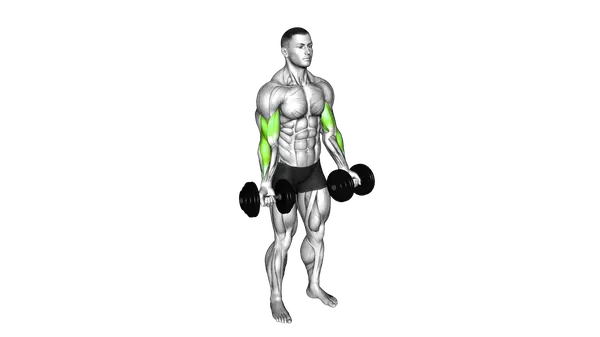
Dumbbell Biceps Curl
The Dumbbell Biceps Curl is a classic strength exercise that builds biceps size and strength with full control and balanced muscle activation.

Dumbbell Concentration Curl
The Dumbbell Concentration Curl isolates the biceps with strict form, helping you build peak strength, control, and muscle definition.
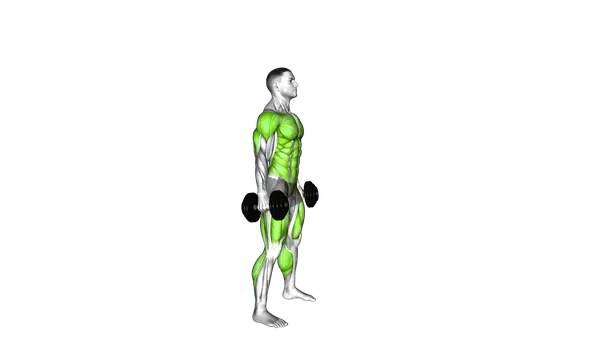
Dumbbell Devils Press
The Dumbbell Devil’s Press is a full-body exercise that combines strength, explosive movement and intense cardio effort.

Dumbbell Hammer Curl
The Dumbbell Hammer Curl stands as a cornerstone bicep and forearm exercise that deserves a place in any comprehensive arm training routine. This variation of the traditional curl uniquely targets the brachialis muscle (which lies beneath the biceps) and the brachioradialis in the forearm, while still engaging the biceps brachii. By maintaining a neutral grip throughout the movement, where palms face inward toward each other rather than upward, the hammer curl creates balanced development across multiple muscle groups in the arms. Perfect for beginners entering the world of resistance training, the hammer curl serves as an approachable yet effective exercise that requires minimal equipment and technical knowledge. This accessibility makes it an ideal starting point for those new to bodybuilding or strength training, providing immediate feedback in terms of muscle engagement and progression potential. The neutral grip position also tends to be more comfortable for those with wrist issues who might find traditional supinated curl positions uncomfortable. For bodybuilding enthusiasts, hammer curls offer that coveted three-dimensional arm development by specifically targeting the often-neglected brachialis and forearms. When these muscles are well-developed alongside the biceps, they create that full, impressive arm appearance from all angles. The exercise particularly shines in creating that visible separation between biceps and triceps when viewed from the side. From a strength perspective, hammer curls contribute significantly to functional arm power. The neutral grip position mimics many everyday lifting motions, translating to improved strength for activities ranging from carrying groceries to moving furniture. Additionally, stronger forearms enhance grip strength, which becomes a limiting factor in many other compound exercises like deadlifts, rows, and pull-ups. Whether incorporated into an arm-specific training day or added to a full-body workout, the dumbbell hammer curl delivers exceptional value for its simplicity. By progressively increasing weight while maintaining proper form, even beginners can experience noticeable improvements in both arm aesthetics and functional strength capacity over relatively short time periods.

Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl
The Dumbbell Incline Alternate Hammer Curl builds arm strength with controlled, alternating reps and constant tension on the biceps.

Dumbbell Incline Bench Row
The Dumbbell Incline Bench Row is a back-focused strength exercise that targets the upper back while reducing lower-back strain.
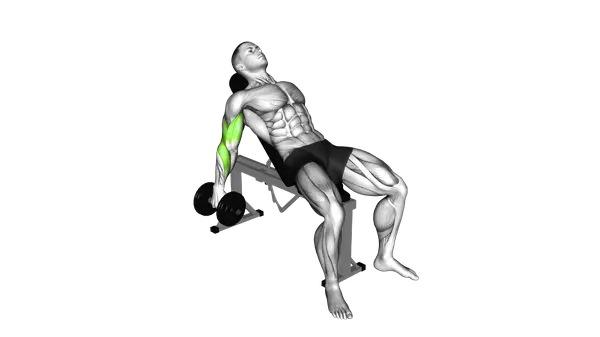
Dumbbell Incline Biceps Curl
The Dumbbell Incline Biceps Curl isolates the biceps through a deep stretch and strict form to maximize muscle growth and control.
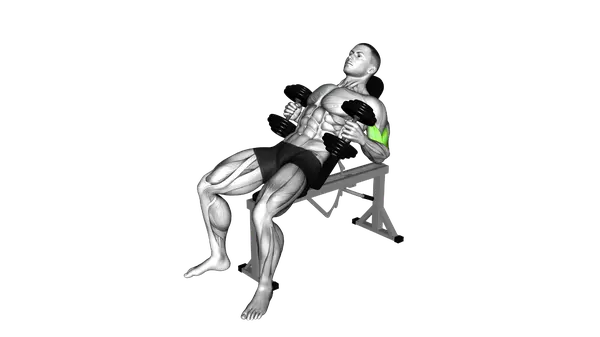
Dumbbell Incline Hammer Curl
The Dumbbell Incline Hammer Curl builds arm strength with a neutral grip, emphasizing control, balance and forearm involvement.

Dumbbell One Arm Preacher Hammer Curl
The Dumbbell One Arm Preacher Hammer Curl is a controlled single-arm exercise that helps improve arm strength and balance.

Dumbbell Single Arm Bent Over Row
The Dumbbell Single Arm Bent Over Row builds back strength and control while improving muscle balance through unilateral pulling.

Dumbbell Suitcase Carry
The Dumbbell Suitcase Carry is a simple loaded walk that builds core control and posture by carrying weight on one side.

Dumbbell Upright Row
The Dumbbell Upright Row builds shoulder and upper-back strength by lifting the weights close to the body in a controlled motion.
Improve grip strength, wrist stability, and muscular endurance
Training goals for forearm development
The primary goals of forearm training are to build crushing grip strength, improve wrist support, and increase muscle density in the lower arms. Forearms respond well to both heavy resistance and high-rep time-under-tension work. Most forearm exercises emphasize wrist flexion, extension, and static holds to challenge smaller stabilizing muscles. With consistent volume and smart progression, you’ll develop strength that carries over to rows, deadlifts, and everyday tasks.
Best forearm exercises for strength and size
Movements to build stronger and more defined forearms
The best forearm exercises include dumbbell wrist curls over bench, barbell reverse curls, farmer’s carries, plate pinches, and static barbell holds. Hammer curls and towel grip rows also activate the forearms alongside the biceps. For isolation work, seated wrist curls and wrist rollers provide focused tension across wrist flexors and extensors. Carry-based exercises like trap bar holds not only build grip strength but also increase vascularity and muscular endurance in the forearms.
Equipment options for forearm training
Train forearms with dumbbells, barbells, bands, or just a towel
Forearm exercises can be performed using barbells, dumbbells, kettlebells, resistance bands, grip trainers, or even household items like towels and plates. Barbells allow for heavy static holds and wrist curls, while dumbbells are ideal for reverse curls and wrist isolations. Resistance bands work well for high-rep burnout sets or rehab-focused routines. If you’re training at home, towel rows or suitcase carries can still activate the entire forearm region effectively.
How to program forearms for strength and function
Integrate forearm exercises into your routine
You can train forearms 1–3 times per week depending on your split and grip demands in other lifts. Many lifters add them to pull or arm days, or use them as finishers after compound lifts. Begin with carry or hold-based movements, then finish with curls and isolations. Focus on consistent time under tension and proper wrist control to avoid strain. Forearms recover quickly, so they respond well to frequent low-to-moderate volume work across the week. Create your personal training program in the app tailored to your goals, fitness level, and schedule. Your plan will include the most effective forearm exercises and show you exactly how to integrate them into your weekly training split.
Frequently asked questions about forearm exercises
Forearms can be effectively trained on either arm or back day, depending on your split and training goals. On back day, they naturally get worked during pulling movements, so it can be convenient to add grip-intensive exercises as a finisher. On arm day, you can focus more on isolation work like wrist curls or reverse curls without fatigue from bigger lifts. You could also dedicate a short standalone session if forearm development is a priority.
Yes, forearm exercises are one of the best ways to improve grip strength. Movements like farmer’s carries, plate pinches, and static barbell holds directly train your ability to grip and hold weight for extended periods. Strengthening the forearms also supports better control in compound lifts like deadlifts and pull-ups. A stronger grip can translate to improved performance across many other exercises and reduce injury risk in the wrists and elbows.
You can train your forearms 1–3 times per week, depending on your overall program and how much indirect volume they already receive from other lifts like pull-ups, deadlifts, and rows. If your main lifts already involve significant grip work, 1–2 focused sessions might be enough. If grip is a weakness or you're specifically aiming to grow your forearms, consider adding isolation exercises or loaded carries more frequently, using moderate volume to avoid overtraining.
Yes, forearms can be effectively trained without traditional gym equipment. Bodyweight exercises like dead hangs from a bar or towel rows can target grip and endurance. You can also do isometric holds with household objects such as water jugs or bags of rice. Even simple movements like squeezing a towel or carrying loaded grocery bags for distance help activate forearm muscles and improve strength over time.
The most effective forearm exercises include wrist curls, reverse curls, and farmer’s carries. Wrist curls target the flexor muscles, while reverse curls hit the extensors and also involve the brachioradialis. Farmer’s carries challenge grip strength and endurance by forcing your forearms to maintain control under load. Plate pinches, wrist rollers, and barbell holds are also excellent additions to build strength, definition, and muscle endurance in the lower arms.
Integrate forearm exercises into full-body and split routines






