Exercises to lift, shape and strengthen the lower glutes
Lower glutes exercises
The lower glutes are crucial for creating that lifted, round appearance and for generating force during hip extension. Targeting this area helps develop glute-hamstring separation, improves balance, and supports athletic power. This overview highlights the most effective lower glute exercises: both compound and isolation, and how to train them at home or in the gym using minimal equipment.
Focus on
Pick your equipment

90/90 Stretch
The 90/90 Stretch improves hip mobility and control by guiding your hips through a stable, seated rotation position.

Assault Bike Run
The Assault Bike Run is a full-body conditioning movement that uses steady pedaling and pushing to build stamina and work capacity.
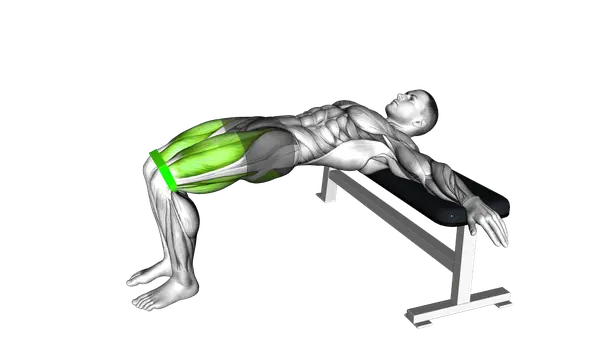
Banded Hip Thrusts
Banded Hip Thrusts are a lower-body strength exercise that builds glute power and tension through band resistance.

Barbell Clean And Jerk
The Barbell Clean and Jerk is an explosive full-body lift that builds power, coordination and total-body strength in one fluid movement.

Barbell Deadlift
The Barbell Deadlift is a foundational strength exercise that builds full-body power and proper lifting mechanics and improves control.
Built for Progress
Take the Guesswork Out of Training
Create personalized AI-powered workout plans that evolve with you. Train smarter, track every rep and keep moving forward.

Barbell Front Squat
The Barbell Front Squat is a lower-body strength exercise that builds quad strength while reinforcing an upright, stable squat position.
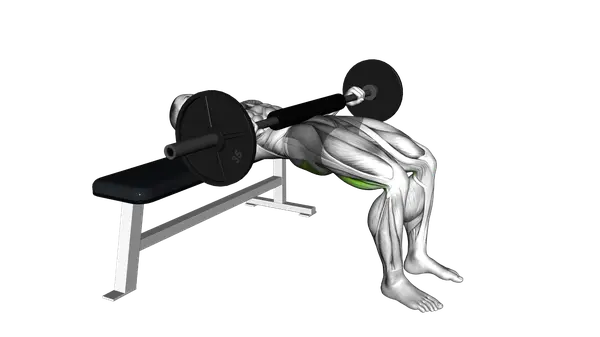
Barbell Hip Thrust
The Barbell Hip Thrust is a compound lower-body strength exercise that builds glute power through loaded hip extension.

Barbell Lunge
The Barbell Lunge is a compound lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, balance and control through unilateral loading.

Barbell Squat
The Barbell Squat is a compound lower-body strength exercise that builds leg power, full-body strength and movement control.

Barbell Step Up
The Barbell Step Up is a lower-body strength exercise that builds leg power, balance, and control through stepping under load.

Barbell Sumo Deadlift
The Barbell Sumo Deadlift is a compound strength exercise that builds lower-body power with a wide stance and upright torso.
Bent Knee Glute Kickback
The Bent Knee Glute Kickback is an isolation exercise that targets the glutes and helps improve hip control and muscle activation.
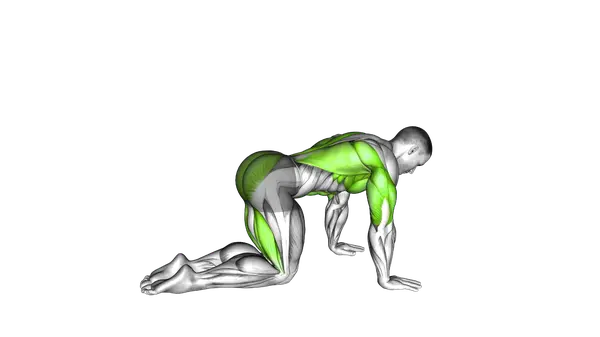
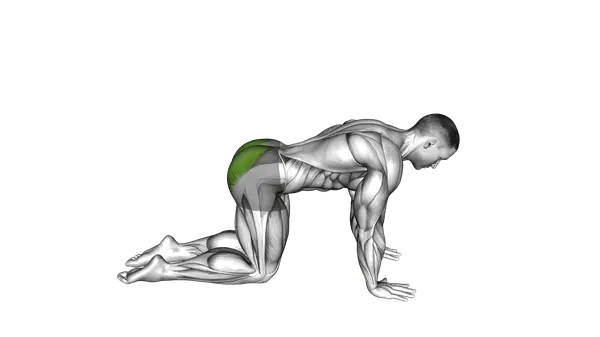
Bird Dog
The Bird Dog is a core stability exercise that improves balance, spinal control, and coordination using slow, controlled movements.

Bodyweight Single Leg Deadlift
The Bodyweight Single Leg Deadlift is a balance-focused exercise that strengthens the hips and legs while improving control.
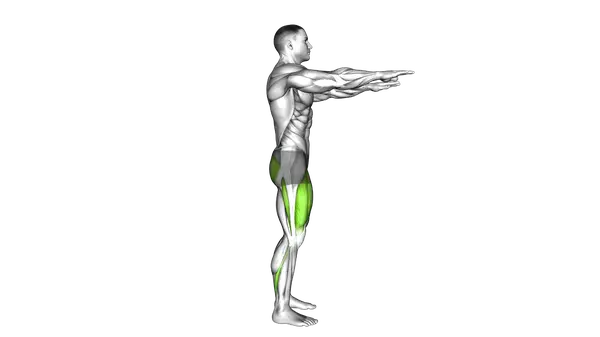
Bodyweight Squat
The Bodyweight Squat is a foundational lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, mobility and movement control.

Bodyweight Step Up
The Bodyweight Step Up is a lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, balance and control using a simple stepping motion.

Bulgarian Split Squat
The Bulgarian Split Squat is a lower-body exercise that builds leg strength, balance, and control by training one leg at a time.
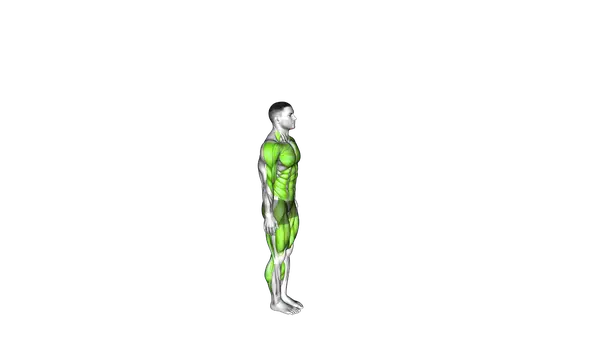
Burpee
The Burpee is a full-body exercise that builds conditioning, strength, and coordination through a fast, continuous movement.
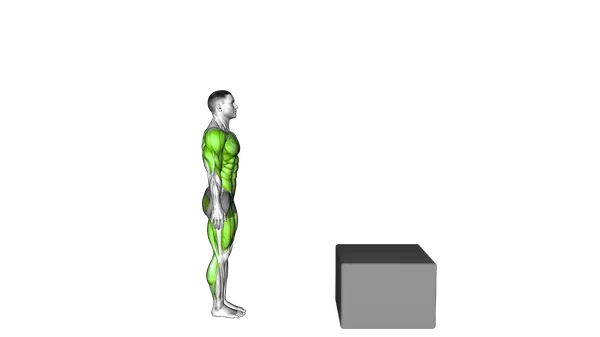
Burpee Box Jump
The Burpee Box Jump combines a burpee with an explosive box jump to build full-body power, coordination, and high-intensity conditioning.

Cable Donkey Kickback
The Cable Donkey Kickback is a cable-based isolation exercise that targets the glutes with constant tension and controlled hip extension.
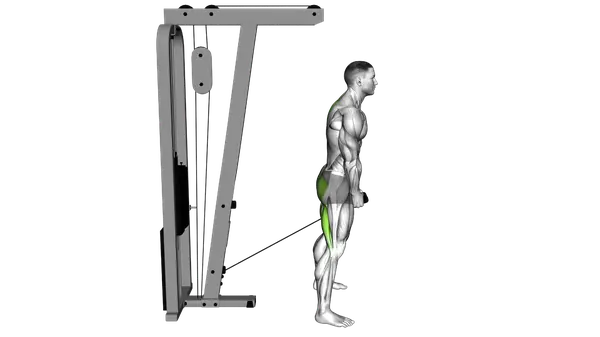
Cable Pull Through
The Cable Pull Through is a cable-based hip hinge exercise that trains the glutes and hamstrings with constant tension and low spinal load.

Cable Standing Hip Extension
The Cable Standing Hip Extension is a cable-based exercise that isolates the glutes and builds controlled hip strength with steady resistance.
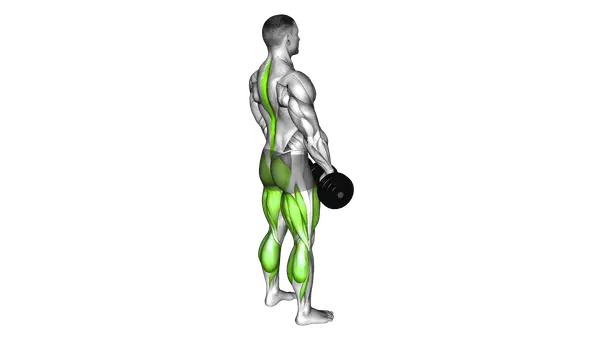
Dumbbell Deadlift
The Dumbbell Deadlift is a full-body strength exercise that builds the glutes, hamstrings, and back while reinforcing proper hip hinge mechanics.

Dumbbell Decline Lying Leg Curl
The Dumbbell Decline Lying Leg Curl is an isolation exercise that targets the hamstrings by adding resistance through a controlled movement.

Dumbbell Front Squat
The Dumbbell Front Squat is a compound lower-body exercise that builds leg strength while encouraging an upright squat position.
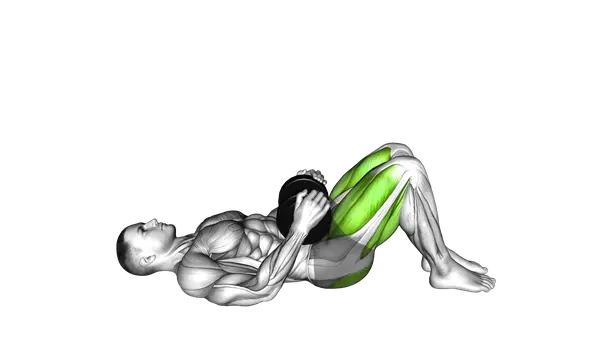
Dumbbell Glute Bridge
The Dumbbell Glute Bridge Chest Press combines a glute bridge with a press to build full-body strength and coordination.
Lift the glutes, define the lower body, and boost athletic power
Training goals for lower glute development
Developing the lower glutes enhances not just how your physique looks from behind, but also how well your hips function in movement. Strengthening this region helps improve sprinting, jumping, and explosive movements while providing greater pelvic stability. Whether your goal is aesthetics, strength, or injury prevention, training the lower glutes delivers results you can see and feel.
Use deep range of motion and tension-based movements
Best lower glute exercises for growth and activation
Some of the best lower glute exercises include deep barbell hip thrusts, glute bridges with elevation, cable kickbacks at a low angle, and deficit reverse lunges. These movements increase stretch and engagement in the lower portion of the glute. You can also incorporate frog pumps, step-ups, and single-leg RDLs to isolate and fully contract the lower glutes. Focus on full range of motion, slower eccentrics, and mind-muscle connection to maximize activation.
Train effectively with bands, benches, cables, or bodyweight
Equipment options for lower glute training
Lower glutes can be trained using various equipment setups: or none at all. A flat bench, resistance bands, or cable machine can be used to adjust angles and target the glutes from below. At home, a raised surface and mini loop bands allow you to mimic these positions. Even simple tools like a yoga mat or a step can support lower-glute-focused bodyweight exercises if you're training without machines or free weights.
Add lower glute focus to leg day or glute-specialized routines
Training plans featuring lower glute exercises
You don’t need an entire session dedicated to lower glutes, but it’s smart to include 2–3 focused exercises per week. Add them into lower-body days or as accessories following compound lifts. They work well at moderate to high reps for activation and shaping.
The app helps you create a personalized training plan that aligns with your goals: whether that’s building muscle, gaining strength, or improving balance: and includes the right exercises based on your experience and available equipment.
Frequently asked questions about lower glute exercises
Yes, training the lower glutes can enhance the visual distinction between the glutes and hamstrings — often called the glute-ham tie-in. Exercises that emphasize range, angle, and isolation help define this area over time. Combined with proper nutrition and overall fat loss, lower glute development improves the shape and contour of the back side.
Lower glutes can be trained 2–3 times per week, either directly through targeted movements or indirectly during compound lower-body exercises. They respond well to moderate volume and higher time under tension. As with any muscle group, recovery is important — aim for at least 48 hours between direct sessions.
Yes, you can train lower glutes at home using bodyweight and resistance bands. Exercises like frog pumps, single-leg glute bridges, banded donkey kicks, and step-ups are effective when done with control and high reps. A raised surface (like a bench or chair) adds range of motion and tension, helping to better target the lower part of the glutes.
Many people struggle to engage the lower glutes because other muscles — like the quads or hamstrings — tend to take over. Focusing on your form, using slower reps, and pausing at peak contraction can improve activation. You may also benefit from warm-up sets or glute pre-activation drills using bands to wake up the area before heavy work.
Top lower glute exercises include deficit reverse lunges, deep barbell hip thrusts, elevated glute bridges, and cable kickbacks at a low angle. These movements stretch and contract the lower portion of the glutes, helping to improve both shape and strength. Combining compound and isolation work leads to the best results.
Integrate lower glute exercises into full-body and split routines



